How to Prevent Cyber Security Attacks

Businesses and consumers around the world are constantly facing the risk of cybersecurity attacks from cybercriminals who try to access and misuse sensitive information.
A Forbes article on cyber security threats states that 43 percent of global cyber security attacks target small businesses. The reason is small businesses are often unable to implement strong defense systems like larger companies.
To nullify cyber threats, organizations need cyber security experts who can safeguard networks, computer systems, servers, and data. On average, companies spend 10 percent of their budget on cyber security and hire people for the positions, including IT security engineer, cyber security analyst, and information security analyst.
Here we have listed the most common questions and answers on cyber security.
1. How do you define a cyber security threat or vulnerability?
A cyber security threat is a malicious attack by cybercriminals to access a network or systems to steal sensitive data. Cyber threats often include malware, viruses, phishing, data breaches, ransomware, and denial of service attacks.
Cybercriminals carry out these attacks using intrusive software applications to destroy computer systems and access classified data. On most occasions, cybercriminals distribute emails to users in the disguise of email phishing and trick users to give up personal information.
Also, IT networks for businesses may have vulnerability, including firewall vulnerabilities, lack of encryption, or insecure connections. Hackers take the advantage of such weak areas and steal login credentials or financial data by tapping into unsecured Wi-Fi access points.
HackerTrail Insider Tip: Don’t overlook the interest of cyber criminals in your organization. Set security tools to scan for vulnerabilities, web applications, and remote access.
2. What are the typical anomalies to observe when a cyber-attack happens?
An anomaly is a red alert or flag about unusual cyber activities observed on a hacked system. Anomalies could happen in the form of a hidden file or order, an unidentified task running without permission, changed passwords, an unknown presence on a system, etc. It is a high priority to detect anomalies so IT security experts can figure out if a system or a network is infected.
More often than not anomalies happen when someone might have downloaded a file or a folder from a dubious website while browsing or doing research. When anticipating an attack, it is crucial to scan all the files on the network and remove the malicious ones before they cause further harm.
3. What is the difference between IDS and IPS?
In short, Intrusion Detection System (IDS) mainly detects intrusions. The administrator should be on alert while preventing any intrusion. Conversely, the Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) is about finding the threats and preventing them. Both IDS and IPS are components of the network infrastructure.
IDS:
An IDS monitors and detects malicious behavior in a network and provides a diagnostic solution. If the system detects a problem, it alerts the security team to inspect it.
There are five types of IDS:
- Application Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (APIDS)
- Host Intrusion Detection System (HIDS)
- Hybrid Intrusion Detection System
- Network Intrusion Detection System (NIDS)
- Protocol-based Intrusion Detection System (PIDS)
IDS performs two types of detections:
- Signature-based Detection: This type of detection alerts administrators about pre-existing signatures, which classify specific types of threats or malicious behavior.
- Anomaly-based Detection: Anomaly-based detection is more effective as it monitors suspicious or malicious patterns.
IPS:
An IPS functions similarly to an IDS system by detecting threats. The system also responds to the situation. It means an IPS takes action during a potential attack or malicious behavior.
There are four types of IPS:
- Network-based intrusion prevention system (NIPS)
- Host-based intrusion prevention system (HIPS)
- Network behavioral analysis (NBA)
- Wireless intrusion prevention system (WIPS)
IPS performs three types of detections:
- Signature-based Detection: Signature-based detection is about monitoring network packets and comparing them with predefined attack patterns, or “signatures.”
- Statistical Anomaly-based Detection: This type of detection monitors the network traffic and compares it with potential traffic patterns.
- Stateful Protocol Analysis Detection: This method detects protocol deviations by comparing observed abnormalities with pre-determined normal activity profiles.
Differences between IDS and IPS:
| IDS | IPS |
| IDS is a system that detects and monitors cyber threats. But it does not take action on its own. | IPS is a prevention system that takes action like accepting or rejecting a network packet based on the rule set. |
| IDS needs the intervention of a human or another system to review results. | IPS requires its database to get auto-updated periodically with new threat data. |
| The placement of IDS should be after the firewall. | The placement of IPS should be after the firewall device in a network. |
| IDS provides functionalities, such as decoupling detection and reaction. | IPS provides functionalities of supporting detection and reaction. |
| The configuration in IDS is inline mode, usually on layer 2. | The configuration in IPS is an inline mode or as an end host. |
4. What are the latest trends in cyber security attacks?
Here are some of the emerging trends in cyber security attacks that businesses should watch out for.
- Artificial intelligence: AI technology has integrated features that can spot the Internet usage patterns of employees and become targets of social engineering attacks.
- Phishing attacks: Through phishing, hackers dupe users into opening a harmful link. For example, sending a web page similar to a bank’s login page and fooling users to enter their credentials. One way to prevent these attacks is by adding user authentication.
- SQL injection attacks: Using these attacks, hackers can view user lists or obtain admin rights. These threats contain harmful code to sneak into the backend database.
- Man in the Middle attacks: A man in the middle or MITM is another rising threat, which does digital eavesdropping, and then hackers steal personal information.
- Typo squatting: Attackers use common URL misspellings to trick users into visiting dangerous sites.
- Crypto-Malware: Crypto-malware or crypto-mining malware is something that hackers use to steal cryptocurrencies.
- IP theft or unauthorized access: One of these instances can lead to the other. A hacking instance can lead to IP theft.
HackerTrail Insider Tip: Educate your employees about the latest types of cyber-attacks, including Phishing, SQL injection, Malware, and others.
5. Can you explain the brute force attack? How to prevent it?
A brute-force attack is a random method to find the correct password or PIN. Hackers keep trying all the combinations of password credentials.
The common ways to prevent brute-force attacks are below:
- Setting ideal password length.
- Creating a unique and complex password.
- Set a limit on unsuccessful login instances.
6. What are the major security vulnerabilities?
The purpose of most cyber-attacks is to steal financial data or steal money. This is why VPNs and cloud-centered technologies are particularly susceptible to attacks.
The following vulnerabilities need fixing:
- Lack of software update: Keep software applications up-to-date.
- Unencrypted communication & data: Get your data and communications encrypted to protect usernames and passwords.
- No user authentication: Lack of user authentication increases the risks of a data breach, and hackers will likely misuse it.
- Unrestricted access: Unrestricted access to a computer system is an open invitation to hackers to run riot. Get access limited to validated users only.
7. What are the most important technical components of cyber security?
The most important technical components of cyber security are to secure all the possible ways to prevent external threats from sneaking into the network. To do that, a cyber security analyst needs to set up strong passwords, use encryption tools, set multiple firewalls, rename routers and networks, and install private Wi-Fi.
HackerTrail Insider Tip: Provide your remote workers with tethering plans or cellular Wi-Fi hotspots to regulate web access.
8. How will you monitor and log cyber security threats?
The first step would be setting up a monitoring tool for cyber security threats. There are tools such as Splunk and Sumo Logic that search and monitor data and generate alerts for cyber threats and other unusual activities in real-time.
9. How to safeguard servers and networks from cyber threats?
Following the best practices is required when securing computer servers and networks. First, it's crucial to set up a secure connection by creating a unique and strong password from the router setting up a VPN, using encryption, and ensuring the security of Wi-Fi connections.
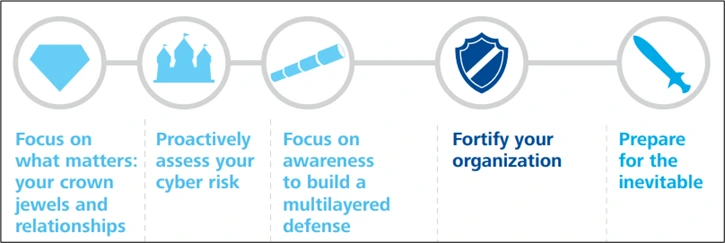
Image Credit: Five Steps to Secure Network & Data (Source: Deloitte.com)
It is also critical to establish a strong authentication system to safeguard login credentials and other sensitive information by using programs such as WatchGuard AuthPoint or Google Authenticator. Besides, using intrusion prevention programs such as Cisco or McAfee, it would be possible to monitor login attempts, particularly for root users.
10. Which three methods do cybercriminals commonly use to breach security and steal information?
Cybercriminals have different methods to execute cyber-attacks. The most common ones are mentioned below:
- Sending phishing emails: A phishing attack happens is when cybercriminals target consumers by sending emails to them which look like reliable sources. Hackers trick the email recipients to provide personal information, such as user ID and password. After getting the data, hackers use the information to access consumers’ accounts to steal confidential data or transfer money.
- Infect a computer network with ransomware: Another method of cybercriminals is to infect a computer or a network of computers with malicious malware which does not let users access systems or files. Hackers ask for a ransom payment to provide access.
- Distributed denial of service (DDoS): DDoS attacks block the access of an online service with excessive traffic from multiple many locations. During a DDoS attack, a website response time slows down and prevents users from accessing the network.
11. What are cyber espionage campaigns and nation-state-sponsored attacks?
Cyber espionage occurs when hackers get unauthorized access to computer networks to steal classified or sensitive information. These attacks are posing challenges for governments and corporations.
Similarly, nation or state-sponsored attacks target governments or authorities to impair a country's economic, political, or military strength. For example, nation-state attacks can steal data on classified military projects or political documents.
12. What do you know about encryption?
The purpose of using encryption is to secure classified data for authorized users only. The five key components of encryption are encryption algorithms, plaintext, secret keys, description algorithm, and ciphertext.
An encryption algorithm can transform the plaintext data into ciphertext with the help of a secret key. By using an encryption tool like BitLocker, it is possible to secure sensitive data on Windows systems and FileVault for Mac.
13. What is malware and how do I get rid of it?
Malicious software or malware in short is something that hackers use to damage the functionalities of a computer, steal data from it, or even gain control of the device.
In most cases, computer users download malware unknowingly by opening an infected file or visiting a malicious website. Once malware is on a system, it launches specific attacks based on its design.
If a system or a network of systems is running slowly or doing unusual activities, it could be due to malware. Run a full anti-virus scan to identify and remove malware from the system or the network.
HackerTrail Insider Tip: Third-party access to your network poses a serious threat through Malware. Restrict third-party access with one-time passwords, manual approvals, and different access rights.
14. How to prevent business email compromise (BEC) incidents?
Business email compromise (BEC) is a criminal activity that targets to scam businesses by convincing them to make wire transfers. These emails appear to come from a familiar source, like an invoice from a supplier.
Companies need to educate their employees about BEC and create an environment where everyone follows a protocol. By taking measures such as optimized controls and monitored networks, companies can protect themselves from such disguised attacks.
15. How to minimize the risk of a cyber security attack
- Having a data backup strategy: Companies should have a strategy of keeping multiple data backups using various technologies and be able to physically remove them from the network. This way, the backup data remains safe if there is a case of a malware infection.
- Implement multi-factor authentication: By requiring multiple factors to prove your identity during the login process, you can drastically reduce the chance of unauthorized access.
- Use advanced threat prevention technologies (ATP): ATP technologies leverage tools such as DNS Filtering, Intrusion Prevention Systems, Next Generation Antivirus (NGAV), Data Encryption, Endpoint Telemetry Data, and Reputation Based Threat Prevention.
- Patching the systems: Businesses should patch or enhance all the systems to prevent hackers from exploiting vulnerabilities.
- Store data in encrypted databases: Companies should store data in encrypted databases to prevent cybercriminals from accessing and stealing the information.
Closing Words
These questions may seem hypothetical, but they let the interviewer have insights into the candidate’s knowledge. You can prepare your answers based on these questions and according to the job description, your priorities, and your objectives.
Think through all the relevant questions from the interviewer’s perspective related to the position and answer them with a step-by-step structure. It will increase your chances of acing the interview.
Backend Technology Interview Questions
C Programming Language Interview Questions | PHP Interview Questions | .NET Core Interview Questions | NumPy Interview Questions | API Interview Questions | FastAPI Python Web Framework | Java Exception Handling Interview Questions | OOPs Interview Questions and Answers | Java Collections Interview Questions | System Design Interview Questions | Data Structure Concepts | Node.js Interview Questions | Django Interview Questions | React Interview Questions | Microservices Interview Questions | Key Backend Development Skills | Data Science Interview Questions | Python Interview Questions | Java Spring Framework Interview Questions | Spring Boot Interview Questions.
Frontend Technology Interview Questions
HTML Interview Questions | Angular Interview Questions | JavaScript Interview Questions | CSS Interview Questions
Database Interview Questions
SQL Interview Questions | PostgreSQL Interview Questions | MongoDB Interview Questions | MySQL Interview Questions | DBMS Interview Questions
Cloud Interview Questions
AWS Lambda Interview Questions | Azure Interview Questions | Cloud Computing Interview Questions | AWS Interview Questions
Quality Assurance Interview Questions
Moving from Manual Testing to Automated Testing | Selenium Interview Questions | Automation Testing Interview Questions
DevOps and Cyber Security Interview Questions
DevOps Interview Questions | Guide to Ethical Hacking | Network Security Interview Questions
Design Product Interview Questions
Product Manager Interview Questions | UX Designer Interview Questions
Interview Preparation Tips
Strength and Weakness Interview Questions | I Accepted a Job Offer But Got Another Interview | Preparation Tips For the Virtual Technical Interview | 7 Tips to Improve Your GitHub Profile to Land a Job | Software Engineer Career Opportunities in Singapore | What can you expect during a whiteboard interview | How To Write A Resignation Letter | Recommendation Letter Templates and Tips.
Quick Links
Practice Skills | Best Tech Recruitment Agency in Singapore, India | Graduate Hiring | HackerTrail Litmus | Scout - Sourcing Top Tech Talent in ONE Minute | About HackerTrail | Careers | Job Openings.



