50+ Must-Know Google Ads Interview Questions and Answers

The Google Ads is an online advertising platform offered by Google. Google allows businesses and advertisers to create and display ads across Google's vast network, which includes Google Search, YouTube, and various partner websites. Google Ads offers several types of ads to suit different advertising goals and target audiences. Here are some of the primary types of Google Ads and their importance:
Different Types of Google Ads:
- Search Ads: Search ads are text-based advertisements that appear at the top or bottom of the SERP page when users search for specific keywords. They are crucial for businesses looking to capture users actively searching for products or services, as they provide high visibility to a targeted audience.
- Display Ads: Display ads are visual banners, images, or videos displayed on websites within Google's Display Network. They help increase brand visibility, generate awareness, and reach a broader audience. They're valuable for creating brand recognition and driving interest.
- Video Ads (YouTube Ads): Video ads are played before, during, or after YouTube videos. They are essential for businesses looking to engage users through video content, build brand awareness, and convey messages through storytelling. They can be skippable or non-skippable.
- Shopping Ads: Shopping ads, often seen on the Google Shopping tab, display product images, prices, and other details. These ads are critical for e-commerce businesses as they showcase products directly to users looking to purchase.
- App Ads: App ads are designed to promote mobile apps and drive installations. They appear on Google Search, YouTube, Google Display Network, and Google Play. They are vital for mobile app developers and businesses looking to increase their app's user base.
- Smart Campaigns: Smart campaigns are simplified Google Ads designed for small businesses. They use automation to create and manage ads, making it easier for companies with limited marketing resources to advertise effectively.
- Local Service Ads: Local Service Ads are tailored for service-based businesses like plumbers, electricians, and locksmiths. They display information such as business hours, services offered, and reviews in local search results, helping users find and contact local service providers.
- Discovery Ads: Discovery ads appear in users' Google Discover feed, Gmail promotions tab, and YouTube home feed. They are designed to capture users' attention while they explore content and can help businesses reach users in moments of inspiration.
- Remarketing Ads: Remarketing ads target users who have previously visited your website or app. They are crucial for re-engaging potential customers and encouraging them to complete desired actions, like purchasing.

The importance of Google Ads lies in its ability to reach a highly targeted audience, measure the effectiveness of campaigns, and adjust advertising strategies in real-time. It provides website traffic, increases brand awareness, generates leads, and boosts sales when used strategically.
Google Ads allows advertisers to set budgets, target specific demographics and locations, and track the performance of their ads, making it a versatile and valuable tool in the digital marketing landscape.
Google Search Network Ads Interview Questions and Answers
1. What are Google Search Ads, and How Does it Work?
Google Search Ads is an online advertising platform developed by Google. It allows businesses and advertisers to display ads within Google search engine results pages (SERPs) and on other Google properties when users enter specific search queries are relevant to their products or services.
These ads are a part of Google's Pay-Per-Click (PPC) advertising, which means advertisers only pay when someone clicks on their ad.
Here's how Google Search Ads works:
- Keyword Selection: Advertisers start by selecting a list of keywords or search terms that are relevant to their products or services. These keywords are the triggers that determine when their ads will be displayed.
- Ad Creation: Advertisers create text-based ads that consist of a headline, description lines, and a URL. The ad content should be engaging and relevant to the chosen keywords.
- Bid Strategy: Advertisers set a maximum bid amount for each keyword. This bid represents the maximum amount they are willing to pay for a click on their ad. Google uses a bidding auction system to determine which ads are shown.
- Quality Score: Google assigns a Quality Score to each keyword-ad combination based on factors like ad relevance, expected click-through rate (CTR), and landing page quality. A higher Quality Score can lead to better ad placement and lower costs.
- Ad Auction: When a user enters a search query matching the selected keywords, Google runs an ad auction. In this auction, Google considers the bid amount, Quality Score, and other factors to determine the ad's Ad Rank.
- Ad Placement: Google displays ads on the SERPs in a specific order based on the Ad Rank. Ads appear at the top and bottom of the search results page. The order of ads can change with each search query and each new auction.
- Clicks and Costs: When a user clicks on an ad, the advertiser is charged a fee, which is deducted from their advertising budget. The cost per click (CPC) can vary depending on the competitiveness of the keyword and the ad's Quality Score.
- Conversion Tracking: Advertisers can track the performance of their ads by setting up conversion tracking. This helps them measure the effectiveness of their campaigns in terms of leads, sales, or other desired actions.
- Campaign Optimisation: Advertisers continually monitor and optimise their campaigns. This includes adjusting bids, refining ad copy, and adding negative keywords to improve the ad's performance.
- Budget Management: Advertisers set a daily or monthly budget to control their ad spending. Once the budget is exhausted, ads will only appear once in the next budget cycle.
Google Search Ads provide advertisers with a powerful tool to reach a highly targeted audience, as ads are displayed to users actively searching for relevant information or products.
2. What are the Key Components of a Google Search Network Ad Campaign?
A Google Search Network ad campaign consists of several key components that work together to create and manage effective advertising campaigns. Understanding these components is essential for setting up and optimising your campaigns.
Here are the key components of a Google Search Network ad campaign:
- Campaign: A campaign is the top-level structure of your advertising efforts. It serves as a container for your ad groups and ads. When you create a campaign, you specify settings such as the budget, location targeting, and start/end dates.
- Ad Group: Within each campaign, you have one or more ad groups. Ad groups are where you organize and group related keywords and ads. Each ad group typically focuses on a specific theme or product category. For example, if you sell both running shoes and hiking boots, you might have separate ad groups for each.
- Keywords: Keywords are the search terms or phrases that trigger your ads to appear when users enter them into Google's search engine. You add keywords to your ad groups and specify match types (e.g., broad match, phrase match, exact match) to control how closely the keyword needs to match the user's search query for your ad to be triggered.
- Ad Copy: Ad copy refers to the text of your ads. Each ad includes a headline, description lines, and a display URL. Ad copy should be compelling, relevant to the chosen keywords, and encourage users to click on your ad.
- Ad Extensions: Ad extensions are additional pieces of information or links that can be added to your ads to provide more context and encourage interaction. Common ad extensions include site link extensions, callout extensions, location extensions, and call extensions.
- Bid Strategy: Bid strategy involves setting how much you're willing to pay for a click (Cost Per Click or CPC) on your ads. You can choose automated bidding strategies that align with your campaign objectives, or you can manually set bids for keywords.
- Quality Score: Quality Score is a metric that Google assigns to your keywords based on factors such as ad relevance, expected click-through rate (CTR), and landing page experience. A higher Quality Score can lead to better ad placement and potentially lower costs.
- Negative Keywords: Negative keywords are terms you specify that you don't want your ads to show for. They help prevent your ads from appearing in irrelevant searches and can improve the overall performance of your campaign.
- Budget: You set a daily or monthly budget for each campaign to control your ad spend. Once your budget is exhausted, your ads will only show once the budget resets.
- Geographic and Demographic Targeting: You can specify the geographic locations and demographics of your target audience. This ensures that your ads are shown to the most relevant users.
- Ad Schedule: You can schedule when your ads should run based on days of the week and times of the day. This allows you to reach your audience when they are most likely to be searching for your products or services.
- Conversion Tracking: Conversion tracking involves setting up goals and tracking actions that are valuable to your business, such as purchases, sign-ups, or phone calls generated by your ads.
- Ad Rotation: Ad rotation settings determine how Google displays your ads when you have multiple ads in an ad group. You can choose to optimise for clicks or evenly rotate ads for testing purposes.
- Ad Position and Ad Rank: Ad position refers to where your ads appear on the search results page. Ad Rank, determined by your bid, Quality Score, and ad relevance, plays a significant role in determining your ad's position.
By understanding and effectively managing these key components, advertisers can create and optimise Google Search Network ad campaigns to reach their target audience and achieve their advertising goals.

3. Explain the Difference Between a Keyword Match Type (Broad Match, Phrase Match, Exact Match) in Google Ads
In Google Ads, keyword match types are used to control how closely the keywords you select for your ads must match the search queries that users enter on Google's search engine. The three primary keyword match types are Broad Match, Phrase Match, and Exact Match.
Broad Match:
- Symbol: No symbol (e.g., keyword)
- Example: If you use the keyword "shoes" as a broad match type, your ad may appear for a wide range of related searches, including "running shoes," "red shoes," and "buy shoes online."
- Matching: Broad match is the most flexible option. It matches your keyword to a broad array of search queries that are related to or have synonyms for your keyword. It can include variations, plurals, misspellings, and related terms.
Phrase Match:
- Symbol: Enclosed in quotation marks (e.g., "keyword")
- Example: If you use the keyword "running shoes" as a phrase match type, your ad may appear for searches like "buy running shoes" or "best running shoes" but not for "shoes for running" or "running sneakers for sale."
- Matching: Phrase match provides more control than broad match. It matches your keyword to search queries that include the exact phrase within quotation marks, but it can have additional words before or after the phrase.
Exact Match:
- Symbol: Enclosed in square brackets (e.g., [keyword])
- Example: If you use the keyword "[blue running shoes]" as an exact match type, your ad will only appear for searches that exactly match the keyword, such as "blue running shoes," with no additional words or variations.
- Matching: Exact match is the most restrictive option. It matches your keyword precisely to the user's search query and doesn't allow for variations, synonyms, or additional words.
Here are some key differences between these keyword match types:
- Control: Broad match provides the least control over which search queries trigger your ads, while exact match offers the most control.
- Reach vs. Precision: Broad match reaches a broader audience but may also result in less relevant clicks. Exact match provides high precision but may limit your ad's reach.
- Negative Keywords: To fine-tune your campaigns, you can use negative keywords (specified with a "-" symbol) to exclude specific terms or phrases for all match types.
In practice, many advertisers use a combination of these match types within their campaigns to strike a balance between reach and relevance. This approach allows them to capture a broad audience with a broad match while maintaining precise targeting for specific keywords using a phrase and exact match types. Keyword match types are essential for optimising your Google Ads campaigns and ensuring that your ads are shown to the most relevant users.
4. What is Quality Score, and Why is It Essential in Google Ads?
Quality Score is a crucial metric in Google Ads that assesses the quality and relevance of your keywords, ads, and landing pages in your advertising campaigns.
It is a rating system used by Google to determine the position of your ads on the search engine results page (SERP) and the cost per click (CPC) you'll pay for each click on your ad.
Quality Score is typically measured on a scale of 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest score.
Quality Score is calculated based on several factors, including:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): The historical CTR of your keyword and ad.
- Ad Relevance: How closely related your keyword is to your ad.
- Landing Page Experience: The quality and relevance of the landing page users reach after clicking your ad.
Improving your Quality Score involves optimising your ad campaigns by creating relevant and high-quality ads, selecting appropriate keywords, and ensuring that your landing pages provide a good user experience.
By focusing on improving your Quality Score, you can enhance the performance of your Google Ads campaigns, reduce costs, and achieve better results.
5. How Do You Create Compelling Ad Copy That Performs Well in the Search Network?
Creating compelling ad copy for the Search Network is essential for driving traffic to your website and achieving your advertising goals.
Here are some tips to help you create ad copy that performs well:
- Understand Your Audience: Start by defining your target audience. Understand their needs, pain points, and preferences. This knowledge will help you craft ad copy that resonates with them.
- Keyword Research: Identify relevant keywords for your ad campaign. These keywords should be included in your ad copy to increase relevance and quality score.
- Unique Selling Proposition (USP): Highlight what sets your product or service apart from the competition. What benefits or solutions do you offer that others don't? Your USP should be front and center in your ad copy.
- Clear and Concise Headlines: Write concise and attention-grabbing headlines. Include keywords and your USP if possible. A strong headline can significantly impact click-through rates (CTR).
- Use Ad Extensions: Take advantage of ad extensions like site links, callouts, and structured snippet extensions. These provide additional information and make your ad more compelling.
- Benefits Over Features: Focus on the benefits of your product or service rather than just listing features. Explain how it can solve the user's problem or fulfill their needs.
- Emotional Appeal: Tap into the emotions of your audience. Craft ad copy that resonates on an emotional level. People often make decisions based on emotions.
- Include a Call to Action (CTA): Encourage users to take action with a clear and compelling CTA. Use action-oriented words like "buy," "shop," "learn more," or "get started."
- A/B Testing: Create multiple ad variations and test them to see which performs the best. Google Ads allows you to run A/B tests to optimise your ad copy.
6. What are Ad Extensions in Google Ads, and Why are They Important?
Ad extensions in Google Ads are additional pieces of information that you can include with your text ads to make them more informative and appealing to potential customers. These extensions expand your ad and provide extra context, links, or contact information, making it easier for users to find what they're looking for and take action.
Here are some common types of ad extensions in Google Ads and why they are essential:
- Sitelink Extensions: These allow you to add additional links to specific pages on your website.
- Callout Extensions: Callout extensions let you add short, descriptive phrases to your ad, highlighting key selling points, offers, or benefits of your products or services.
- Structured Snippet Extensions: These extensions enable you to showcase specific aspects of your products or services in a structured format.
- Call Extensions: Call extensions include a phone number in your ad, allowing users to call your business directly from the ad.
- Location Extensions: If you have a physical storefront or multiple locations, you can use location extensions to display your business address, phone number, and a map marker in your ad.
- Message Extensions: Message extensions add a message icon to your ad, allowing users to send you a text message directly from the ad.
- Price Extensions: Price extensions display a list of your products or services along with their prices.
- Promotion Extensions: These allow you to highlight special offers, discounts, or promotions in your ads.
Ad extensions are essential for several reasons:
- Improved Ad Visibility
- Enhanced Relevance
- Higher Click-Through Rates (CTR)
- Better Quality Score
- Increased Conversions
Ad extensions in Google Ads are valuable tools that enhance your ad's visibility, relevance, and performance. They are essential for optimising your advertising campaigns and providing a better experience to potential customers.
7. Explain the Concept of Ad Rank in Google Ads
Ad Rank is a crucial concept in Google Ads that determines the position of your advertisements in search engine results pages (SERPs) and the overall success of your ad campaigns.
Ad Rank is calculated in real-time each time a user conducts a search query that triggers an ad auction.
The formula for calculating Ad Rank is as follows:
Ad Rank = Quality Score x Max CPC Bid
Let's break down these two components:
- Quality Score: Quality Score is a metric that assesses the quality and relevance of your ad, keywords, and landing page to the user's search query. It is scored on a scale of 1 to 10, with 10 being the highest possible score. Google uses various factors to calculate Quality Score, including.
- Click-through rate (CTR): The historical performance of your ads in terms of how often they are clicked compared to how often they are shown.
- Ad relevance: How closely your ad copy relates to the keywords you are bidding on.
- Landing page quality: The quality and relevance of the page users are directed to when they click on your ad. A higher Quality Score typically leads to a better Ad Rank and can help your ad appear higher in search results, even if your bid is lower than competitors.
- Max CPC Bid: This is the maximum amount you are willing to pay for a click on your ad. It represents the highest bid you set for a specific keyword or ad group.
8. What is the Difference Between CPC (Cost Per Click) and CPM (Cost Per Mille) bidding in Google Ads?
CPC (Cost Per Click) and CPM (Cost Per Mille) are two different bidding strategies in Google Ads, each with its advantages and use cases.
Here's a breakdown of the key differences between CPC and CPM bidding:
| CPC (Cost Per Click) | CPM (Cost Per Mille) | |
| Billing Model | In CPC bidding, advertisers are charged each time a user clicks on their ad. You set a maximum CPC bid, which is the most you're willing to pay for a single click on your ad. You're charged only when someone clicks on your ad, regardless of how many times it's displayed (impressions). | CPM bidding, on the other hand, charges you based on the number of ad impressions (views) your ad receives. The term "Mille" refers to one thousand impressions. You specify how much you're willing to pay for every 1,000 ad impressions. |
| Objective | CPC bidding is often used when the primary goal is to drive traffic to a website, generate leads, or encourage specific actions, such as form submissions or product purchases. Advertisers are more interested in getting users to click on their ads. | CPM bidding is typically used when the primary goal is to increase brand visibility and awareness. Advertisers want their ads to be seen by as many people as possible, and they are less concerned about clicks or direct user interactions. |
| Ad Placement Control | With CPC bidding, you have more control over where your ads appear because you only pay when someone clicks. You can optimise your campaign for specific keywords, audiences, or placements to drive more clicks. | CPM bidding should be more focused on where your ads appear because you pay for impressions. It's more suitable for campaigns where you want broad exposure and are more relaxed about specific clicks or user interactions. |
| Performance Metrics | CPC bidding provides clear metrics for measuring the effectiveness of your campaign, such as click-through rate (CTR), conversion rate, and return on ad spend (ROAS). | CPM bidding is more about exposure and branding, so metrics like reach, frequency, and impressions per dollar spent are more relevant. |
| Budget Flexibility | CPC bidding can be more budget-friendly for advertisers with a limited budget because they only pay when someone clicks. You have more control over your ad spend. | CPM bidding may require a higher budget because you're paying for impressions, and you may need immediate direct returns in terms of clicks or conversions. |
| Ad Content | Ad content in CPC campaigns often emphasises compelling calls to action to encourage clicks. | Ad content in CPM campaigns may focus more on branding and conveying a message since the goal is to maximise impressions. |
9. How Do You Optimise a Google Ads Campaign for Better Performance and ROI?
Optimising a Google Ads campaign for better performance and ROI (Return on Investment) involves a combination of strategic planning, ongoing monitoring, and tactical adjustments.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to optimise your Google Ads campaign:
- Set Clear Goals and KPIs (Key Performance Indicators).
- Keyword Research
- Ad Copy and Ad extension optimisation
- Landing Page Optimisation
- Ads Budget Management
- Ad Scheduling and Geo-Targeting Optimisation
- Quality Score Improvement
- Competitive Analysis
- Ad Testing
- Conversion Tracking Setup
- Regularly Monitor and Adjust campaign performance
- Analytics Tools Setup.
- Remarketing Campaign Creation.
- Adherence to Google Ads Policies.
- Stay Up to Date knowledge about Google ads.
10. What are Negative Keywords, and Why are They Useful in Google Ads?
Negative keywords are specific words or phrases that you can add to your Google Ads campaign to prevent your ads from showing when those keywords are included in a user's search query. In other words, they are the opposite of regular (positive) keywords, which trigger your ads to display when they match a user's search.
Here's why negative keywords are helpful in Google Ads:
- Improving Relevance
- Cost Savings
- Enhancing Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Better Targeting
- Reducing Ad Impressions
- Avoiding Irrelevant Clicks
11. How Do You Track and Measure the Success of a Google Ads Campaign?
Tracking and measuring the success of a Google Ads campaign is essential to ensure that you're getting a good return on your advertising investment.
Here are the key steps to track and measure the success of a Google Ads campaign:
- Define Your Goals and KPIs: Before you start your campaign, clearly define your goals. What do you want to achieve with your Google Ads campaign? Common goals include increasing website traffic, generating leads, boosting sales, or raising brand awareness.
- Set Up Conversion Tracking: Implement conversion tracking on your website. Google provides a code snippet (known as a conversion tracking tag) that you need to add to the relevant pages where conversions occur (e.g., thank-you pages after form submission or purchase).
- Link Google Analytics: Connect your Google Ads account to Google Analytics. This integration provides more detailed insights into user behavior on your website and helps you analyse how your ads are performing in terms of bounce rates, time on site, and more.
- Use UTM Parameters: Utilise UTM parameters in your ad URLs to track the source and medium of traffic accurately. This will help you understand which ads and keywords are driving the most conversions.
- Monitor Click-Through Rate (CTR): CTR is a critical metric that indicates the effectiveness of your ad copy and its relevance to your target audience. A higher CTR generally means your ads are resonating with users.
- Analyse Conversion Data: Regularly review conversion data in your Google Ads account. Track the number of conversions, conversion rate, and cost per conversion. These metrics help you understand how well your campaign is meeting your goals.
- Measure Return on Ad Spend (ROAS): If your primary goal is to generate sales, calculate the ROAS to determine how much revenue you're generating for every dollar spent on advertising. It's a crucial metric for assessing the profitability of your campaigns.
- Assess Quality Score: Google assigns a Quality Score to each keyword in your campaign. A higher Quality Score can lead to lower costs and better ad placements. Keep an eye on this metric and work to improve it by optimising your ads and landing pages.
- Review Search Terms: Regularly check the search terms report to see which search queries triggered your ads. This helps you identify irrelevant keywords and negative keywords that should be added to your campaign to improve targeting.
- Regular Reporting: Create regular reports or dashboards to track campaign performance over time. This allows you to identify trends and make data-driven decisions for optimisation.
12. What is the Google Ads Editor, and How Can It Be Beneficial for Managing Campaigns?
Google Ads Editor is a free desktop application offered by Google that is designed to help advertisers efficiently manage their Google Ads campaigns. It provides a range of features and benefits for campaign management.
Here's an overview of what Google Ads Editor is and how it can be beneficial:
- Offline Campaign Management: Google Ads Editor allows you to work on your campaigns offline. You can download your Google Ads account data, make changes, and then upload those changes when you have an internet connection.
- Bulk Editing: With Google Ads Editor, you can easily make bulk changes to your campaigns, ad groups, keywords, ad copy, and more.
- Advanced Search and Filtering: The application offers advanced search and filtering options that make it easier to locate specific ads, keywords, or other elements within your campaigns.
- Copy and Paste: You can copy items (e.g., keywords, ads, ad groups) within your account or across different accounts, making it simple to replicate successful elements of your campaigns.
- Account Structure: Google Ads Editor provides a visual representation of your account's structure, making it easier to organize and restructure your campaigns and ad groups.
- Import and Export: You can import and export campaigns, ad groups, and other elements in bulk using CSV files.
13. Can you Explain the Difference between Search Network and Display Network Campaigns in Google Ads?
Google Ads offers two primary types of advertising campaigns: Search Network and Display Network. These two campaign types serve different purposes and target audiences.
Here's a breakdown of the key differences between them:
| Search Network | Display Network | |
| Placement and Purpose | In Search Network campaigns, your ads appear on Google search engine results pages (SERPs) when users enter relevant search queries. These ads are text-based and are designed to capture users actively searching for specific products, services, or information. | Display Network campaigns, on the other hand, display ads on websites, mobile apps, and videos within Google's vast network of partner sites. These ads can be text, image, video, or interactive media and are often used for brand awareness, reaching a broader audience, and visually showcasing products or services. |
| Ad Format | Ads in Search Network campaigns are typically text-based and consist of a headline, description lines, and URL. They are displayed at the top and bottom of Google search results, making them highly relevant to the user's search query. | Display Network ads come in various formats, including banner ads, image ads, video ads, and interactive ads. These ads are more visually appealing and can be displayed on websites and apps across the internet. |
| Keyword Targeting | Search Network campaigns primarily rely on keyword targeting. You select keywords relevant to your business, and your ads are triggered when users search for those specific keywords. | Display Network campaigns use contextual targeting, audience targeting, or placement targeting. Contextual targeting matches your ads to thematically relevant website content. Audience targeting lets you choose specific demographics, interests, and behaviors of the audience you want to reach. Placement targeting allows you to select specific websites or apps where you want your ads to appear. |
| User Intent | Users on the Search Network are actively searching for something, indicating a higher level of intent to make a purchase or find specific information. This makes Search Network campaigns more suitable for capturing leads or converting users with immediate needs. | Display Network campaigns target users who may not have an immediate intent to purchase but can be influenced by your ads. These campaigns are often used for building brand awareness, retargeting, and reaching users earlier in the buying cycle. |
| Costs and Click-Through Rates (CTR) | Search Network campaigns tend to have higher CTRs and can be more expensive per click because users are actively seeking information or products related to your ads. | Display Network campaigns typically have lower CTRs and can have lower costs per click, but they are more focused on impressions and branding. |
14. Have You Worked with Google Ads Scripts or Automation? If so, Please Provide an Example of How You've Used Them
Google Ads scripts are a way to automate tasks and make changes to your Google Ads campaigns using JavaScript. They can be used to perform various tasks, such as adjusting bids, generating reports, and pausing or enabling keywords or ads based on certain conditions.
Here's a simple example of a Google Ads script that pauses keywords with Quality Scores:
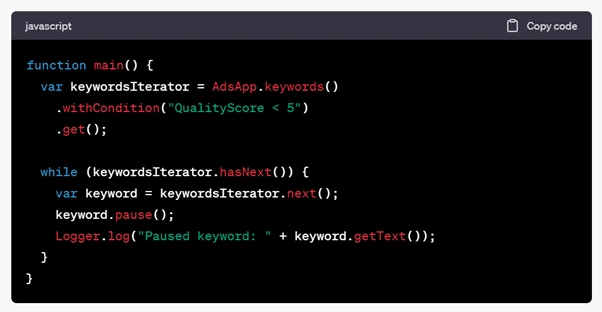
In this example, the script fetches all keywords with a Quality Score of less than 5 and pauses them. It then logs the keywords that were paused.
This is just a basic example, and Google Ads scripts can be customised to perform a wide range of tasks based on your specific needs and objectives. They are a powerful tool for automating routine tasks and optimising your Google Ads campaigns.
15. What are the Best Practices for Mobile Advertising in Google Ads?
Mobile advertising in Google Ads can be highly effective if you follow best practices to reach and engage your target audience.
Here are some tips to help you optimise your mobile advertising campaigns:
- Responsive Ads: Create responsive ads that automatically adjust their size and format to fit different mobile devices and screen sizes. This ensures your ads look good and are readable on various mobile devices.
- Mobile-Friendly Landing Pages: Ensure that the landing pages you link to from your ads are mobile-friendly. They should load quickly and display well on mobile devices. Google's Mobile-Friendly Test tool can help you assess your landing pages.
- Optimise for Mobile Keywords: Mobile users often have different search behaviors. Use Google's Keyword Planner to find mobile-specific keywords and tailor your ad copy to address mobile users' needs and intent.
- Ad Extensions: Utilise ad extensions such as call extensions, location extensions, and site link extensions to provide additional information and options to mobile users. These extensions can make your ads more relevant and engaging.
- Location Targeting: If your business is location-based, use location targeting to reach users in specific geographic areas. This is especially important for mobile advertising, as many users search for local information on their mobile devices.
- Mobile Bid Adjustments: Adjust your bids for mobile devices based on their performance compared to desktops and tablets. You can set bid adjustments in Google Ads to bid more or less aggressively for mobile traffic.
- Ad Scheduling: Analyse when your target audience is most active on mobile devices and schedule your ads accordingly. Use ad scheduling to show your ads at the correct times of the day or week.
By following these best practices, we can create more effective and engaging mobile advertising campaigns in Google Ads and reach your target audience on their mobile devices.
16. How Do You Handle a Situation Where a Campaign is Not Performing as Expected?
Handling a situation where a marketing campaign is not performing as expected can be challenging, but it's also an opportunity to learn, adjust, and potentially turn things around.
Here's a step-by-step guide on how to handle such a situation:
- Analyse the Data: Start by collecting and analysing data related to the campaign's performance. Look at key metrics such as click-through rates (CTR), conversion rates, return on investment (ROI), and any other relevant KPIs.
- Identify the Problem: Determine what exactly is not working as expected. Is it a lack of engagement, high bounce rates, low conversion rates, or something else? Pinpoint the specific issue.
- Review Your Goals and Expectations: Compare the campaign's performance to the initial goals and expectations you set. Were these goals realistic? If not, adjust them to align with the actual performance.
- Check Your Target Audience: Verify that you are reaching the right audience. Sometimes, campaigns underperform because they need to reach the intended demographic.
- Assess Your Messaging and Creative: Review your ad copy, visuals, and messaging. Ensure that they are compelling, clear, and relevant to your target audience. Adjust if needed.
- Evaluate Your Offer or Product: Sometimes, the problem may lie with the product or offer itself. Is there something about your product or service that needs to be resonating with your audience? If so, consider making changes or refining your offer.
- Competitor Analysis: Research what your competitors are doing. Are they running similar campaigns? What strategies are they using? Analysing your competitors can provide insights into what might be missing from your campaign.
- Budget and Bid Strategy: Assess your budget allocation and bidding strategy. It's possible that you need to allocate more resources to the campaign or that your bid strategy needs adjustment.
17. Can you Give an Example of a Successful Google Ads Campaign You've Managed in the Past?
Client: An e-commerce store selling handmade jewellery
Goal: Increase online sales and brand visibility
Strategy
Keyword Research: Conducted thorough keyword research to identify relevant keywords with high search volume and moderate competition related to handmade jewellery.
Campaign Structure:
- Created multiple ad campaigns, each targeting specific product categories (e.g., necklaces, bracelets, earrings).
- Segmented campaigns by match types (broad, phrase, exact) to have precise control over keyword targeting.
Compelling Ad Copy:
- Crafted compelling and unique ad copy for each product category.
- Included relevant keywords in ad headlines and descriptions.
- Highlighted vital selling points such as quality, craftsmanship, and uniqueness.
Landing Page Optimisation:
- They ensured that the landing pages for each ad group were highly relevant to the keywords and ad copy.
- We are focused on user-friendly design and clear calls to action (CTAs).
Ad Extensions:
- We utilised ad extensions like site link extensions to provide additional information and direct users to specific product pages.
For several months, the campaign achieved the following results:
- Increased Sales: Online sales increased by 40% compared to the previous period.
- Improved ROI: Return on ad spend (ROAS) increased by 25%.
- Higher Visibility: The brand's online visibility improved significantly, leading to increased organic traffic as well.
- Lowered Costs: Effective cost per click (CPC) decreased by 15% through ongoing optimisation.
- Positive Customer Feedback: The client received positive feedback about the ad campaigns, with customers highlighting the relevance of the ads to their search queries.
18. What are Some Recent Updates or Changes in Google Ads, and How Do You Think They Impact Advertisers?
- Privacy Changes: Google, like many other online advertising platforms, has been adapting to increased privacy concerns and regulations. This includes the deprecation of third-party cookies and changes in how user data is collected and used for targeting. These changes can impact advertisers' ability to track and target users effectively.
- Automation and Machine Learning: Google has been heavily investing in machine learning and automation in its advertising platform. This includes Smart Bidding strategies, responsive ads, and automated ad extensions. These features aim to make it easier for advertisers to optimise their campaigns but may require a shift in strategy and control for some advertisers.
- New Ad Formats: Google periodically introduces new ad formats, such as Gallery Ads, Discovery Ads, and Video Discovery Ads. These formats can provide new opportunities for advertisers to reach their audience in different ways.
- Expanded Targeting Options: Google Ads has introduced new targeting options, like affinity and in-market audiences, as well as custom intent audiences. These options allow advertisers to refine their targeting and reach specific user segments more effectively.
- Local Advertising: Google has been enhancing its local advertising capabilities with features like Local Services Ads and Google Business Profile updates. These changes are beneficial for businesses with physical locations.
- Attribution Models: Google Ads has been improving its attribution modelling, which helps advertisers understand how different touchpoints contribute to conversions. These updates can help advertisers make more informed decisions about their marketing mix.
- Performance Metrics and Reporting: Google Ads often updates its reporting interface, providing advertisers with more detailed and actionable insights into their campaigns' performance.
- Quality Score Updates: Google has made changes to how the Quality Score is calculated, emphasising the importance of ad relevance and landing page experience. Advertisers need to focus on creating highly relevant ad campaigns.
The impact of these changes on advertisers can vary depending on their specific goals and strategies.
Some advertisers may find these updates beneficial in terms of efficiency and targeting options, while others may face challenges in adapting to new privacy regulations and automation features.
Staying informed about the latest Google Ads updates and how they may affect your advertising efforts is crucial to maintaining a successful online advertising strategy.
Google Display Network Ads Interview Questions and Answers

1. What is the Google Display Network (GDN)?
The Google Display Network (GDN) is a vast advertising network operated by Google that allows advertisers to display their ads on a wide range of websites, mobile apps, and other online platforms.
Key features and components of the Google Display Network include:
- Ad Formats: Advertisers can create various ad formats, including text ads, image ads, video ads, responsive ads, and interactive ads. These ads can appear in different sizes and formats to suit the context of the website or app where they are displayed.
- Targeting Options: Advertisers can target their ads based on various criteria, such as keywords, demographics, location, interests, and user behaviour. This targeting allows advertisers to reach specific audiences likely to be interested in their products or services.
- Placements: Advertisers can choose specific websites, apps, or placements within the GDN where they want their ads to appear. Alternatively, they can use automatic placements, letting Google's algorithms determine the best locations for their ads.
- Remarketing: The GDN allows advertisers to target users who have previously visited their website or interacted with their ads. This is a powerful feature for re-engaging potential customers and encouraging them to complete desired actions.
- Contextual Targeting: Ads can be displayed on websites and apps that have content related to the advertiser's products or services.
- Budget and Bidding Options: Advertisers can set daily budgets and choose from various bidding strategies, such as cost per click (CPC), cost per thousand impressions (CPM), or cost per acquisition (CPA), to control their advertising spend.
- Performance Tracking: The GDN provides comprehensive reporting and analytics tools to monitor the performance of ads, allowing advertisers to optimise campaigns based on real-time data.
- Ad Extensions: Advertisers can enhance their ads with extensions that provide additional information, such as location information, phone numbers, and links to specific pages on their websites.
Overall, the Google Display Network offers advertisers a powerful platform to reach a vast and diverse online audience across millions of websites and apps, making it an integral part of many digital marketing campaigns.
2. What are the Key Advantages of Advertising on the Google Display Network?
Advertising on the Google Display Network (GDN) offers several key advantages for businesses looking to reach their target audience and promote their products or services online:
- Vast Reach: The GDN is one of the largest online advertising networks, with millions of websites, apps, and platforms within its network. This allows advertisers to reach a broad and diverse audience across the internet.
- Targeting Options: GDN provides extensive targeting options to help you reach the right audience. You can target users based on demographics, interests, behavior, location, and more. This precise targeting helps you ensure your ads are shown to the most relevant potential customers.
- Contextual Targeting: Google's contextual targeting technology matches your ads with relevant website content. This means your ads are more likely to be displayed on websites and pages that are related to your products or services, increasing the chances of engagement and conversions.
- Remarketing: GDN allows you to target users who have previously visited your website or interacted with your brand. Remarketing campaigns can be highly effective in re-engaging potential customers who may have yet to convert during their initial visit.
- Multiple Ad Formats: You can use various ad formats on the GDN, including text ads, image ads, video ads, and responsive ads.
- Cost-Effective: GDN often offers lower click costs compared to search advertising. This can be particularly advantageous for businesses with tight budgets, as it allows for cost-effective brand exposure and lead generation.
- Performance Tracking: Google Ads provides robust analytics and reporting tools, allowing you to track the performance of your GDN campaigns in real-time.
- Ad Extensions: You can use ad extensions in GDN campaigns to provide additional information to users and encourage them to take specific actions, such as making a phone call or signing up for a newsletter.
- Flexible Budgeting: Google Ads lets you set daily or campaign-level budgets, giving you control over your advertising spend.
- Cross-Device Targeting: GDN allows you to reach users on various devices, including desktop computers, tablets, and mobile phones, ensuring your ads are visible to potential customers no matter how they access the internet.
- Brand Awareness: For businesses looking to build brand awareness, GDN can be a powerful tool. Display ads can help increase brand recognition and visibility, even if there are other goals than immediate conversions.
- Ad Creation Tools: Google offers tools like the Responsive Display Ad Builder, making it easier for advertisers to create visually appealing and responsive ads without the need for extensive design skills.
3. Explain What Contextual Targeting is in GDN Advertising
Contextual targeting in Google Display Network (GDN) advertising is a strategy that involves displaying ads to users based on the content they are currently viewing on a website or web page.
This targeting method takes into account the context of the web page, including its topics, keywords, and overall theme, to determine which ads are most relevant to the content.
Here's how contextual targeting works in GDN advertising:
- Content Analysis: Google's algorithms analyse the content of web pages across the internet. This analysis includes scanning the text, images, headlines, and other elements on the page.
- Keyword and Topic Identification: The system identifies keywords and topics that are relevant to the content of the web page. It assesses the context of these keywords and topics to understand the page's overall theme.
- Ad Matching: Advertisers create ad groups with specific keywords or topics that are relevant to their products or services. These keywords or topics are then matched with the keywords and topics identified on web pages.
- Displaying Relevant Ads: When a user visits a web page, Google's contextual targeting system matches the page's content to relevant ad groups. If there's a match, it displays ads from the corresponding ad group on that page.
The key benefits of contextual targeting in GDN advertising are:
- Relevance: Ads displayed using contextual targeting are more likely to be relevant to users because they align with the content they are currently engaged with. This can lead to higher click-through rates and better conversion rates.
- Improved User Experience: Users are more likely to find the ads helpful and non-intrusive when they are contextually relevant to the content they are viewing.
- Advertiser Control: Advertisers have control over the keywords and topics they target, allowing them to align their ads with specific content that matches their target audience's interests.
- Brand Safety: Contextual targeting can also be used to ensure brand safety by avoiding placement on web pages with inappropriate or harmful content.
4. What is the Difference Between Placements and Keyword Targeting on the GDN?
In the context of Google Display Network (GDN) advertising, placements and keyword targeting are two distinct methods for reaching your desired audience.
Here's a breakdown of the key differences:
Placements Targeting:
Placement targeting allows you to choose specific websites, apps, or placements within the GDN where you want your ads to appear.
We can select individual websites or choose categories of websites that are relevant to your target audience.
For example, you can choose to display your ads on specific news sites or within the "Travel" category.
Placement targeting offers a high level of control over where your ads will be displayed. It's ideal when you have a good understanding of where your target audience is likely to spend their time online.
Keywords Targeting:
Keyword targeting on the GDN involves selecting keywords that are relevant to your product, service, or content. Google then displays your ads on websites and pages that have content related to those keywords.
This method is similar to how keyword targeting works on the Google Search Network, but on the GDN, it targets the content of websites rather than search queries.
With keyword targeting, your ads can appear on a broader range of websites that have content matching your selected keywords. It's suitable for advertisers looking to reach audiences based on the context of the content they are viewing.
5. What is the Importance of Ad Creativity in GDN Advertising?
Ad creative plays a crucial role in the success of Google Display Network (GDN) advertising campaigns.
The GDN is a vast network of websites, apps, and platforms where our ads can be displayed, making it essential to create compelling and visually appealing ad creatives.
Here are several reasons why ad creative is essential in GDN advertising:
- First Impression: Your ad creative is often the first interaction a potential customer has with your brand or product. A well-designed and engaging ad can grab the user's attention and leave a positive first impression, increasing the likelihood of them clicking on your ad.
- Visibility: GDN ads are displayed alongside content on various websites and apps. To stand out in this crowded digital space, your ad creative needs to be eye-catching and relevant to the content where it's displayed.
- Message Communication: Ad creatives convey your message, product, or service to your target audience. Compelling ad copy and visuals can succinctly communicate the value proposition of your offering and encourage users to take the desired action, such as clicking through to your website.
- Relevance: Tailoring your ad creative to the interests and demographics of your target audience can significantly improve ad relevance. GDN offers targeting options, and matching your creative to these parameters can enhance your campaign's effectiveness.
- Brand Image: Your ad creative should align with your brand's identity and values. Consistent branding across ads helps build brand recognition and trust among potential customers.
- Click-Through Rate (CTR): Ad creatives directly impact your ad's CTR, which is a critical metric for GDN campaigns. A high CTR indicates that your ad is resonating with users, leading to more traffic and potential conversions.
- Quality Score: Google uses a Quality Score system to assess the relevance and quality of your ads. Ad creative, including ad relevance, click-through rate, and landing page experience, is a significant factor in determining your Quality Score. A higher Quality Score can lead to lower costs per click and improved ad placement.
- Ad Variations: Testing different ad creatives allows you to optimise your campaign performance. A/B testing different ad elements (such as headlines, images, and calls to action) can help you identify what resonates best with your audience and refine your strategy accordingly.
- Mobile-Friendly Design: As a significant portion of GDN traffic comes from mobile devices, creating mobile-responsive ad creatives is essential to ensure that your ads look and perform well on smaller screens.
6. How Can You Optimise a GDN Campaign for Better Performance?
Optimising a Google Display Network (GDN) campaign for better performance involves a combination of strategies and tactics to improve targeting, ad creative, bidding, and overall campaign management.
- Set Clear Objectives
- Audience Targeting
- Keyword Targeting
- Ad Placements
- Ad Creative
- Ad Copy and Messaging
- Landing Page Optimisation
- Bidding Strategy
- Budget Management
- Ad Scheduling
- Frequency Capping
- Conversion Tracking
- A/B Testing
- Quality Score Improvement
- Remarketing
- Competitive Analysis
- Regular Monitoring and Reporting
- Ad Compliance
- Mobile Optimisation
- Experimentation and Learning
Optimising a GDN campaign is an ongoing process. Regularly review and refine our strategies based on performance data to achieve better results over time.
7. What is the Importance of Ad Extensions in GDN Advertising?
Ad extensions are an essential component of Google Display Network (GDN) advertising for several reasons:
- Enhanced Visibility
- Improved Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Increased Relevance
- Better Ad Rank
- Enhanced User Experience
- Measurable Results
- Competitive Advantage
- Ad Format Variety
Ad extensions play a crucial role in GDN advertising by enhancing the visibility, relevance, and user experience of your ads. They can lead to higher CTRs, better ad ranks, and improved overall campaign performance, making them an essential tool for advertisers looking to maximise the impact of their display network ads.
8. Explain the Concept of Viewability in GDN Advertising
Viewability is an essential metric in online advertising, including in the Google Display Network (GDN).
It refers to whether an ad was actually seen by a user when it was displayed on a webpage. In other words, it measures the likelihood that an ad could be viewed by a real user.
Here are some key points to understand about viewability in GDN advertising:
Definition:
Viewability is typically measured as a percentage and is defined by industry standards. The Interactive Advertising Bureau (IAB) and the Media Rating Council (MRC) have established guidelines for viewability.
According to these guidelines, an ad is considered viewable when at least 50% of its pixels are in the viewable space of the user's browser for at least one second for display ads.
For video ads, it's typically considered viewable if at least 50% of the video player is in the viewable space for at least two seconds.
Viewable Impressions:
Advertisers are interested in viewable impressions, which are the number of times users see their ads.
It's different from total impressions, which count all instances of the ad being served, whether it was in the viewable area.
Factors Affecting Viewability:
Several factors can influence viewability, including ad placement, ad size, ad format, website design, and user behaviour.
Ads that are placed higher on a webpage, are more prominent, and have engaging content are more likely to be viewable.
Importance:
Viewability is crucial for advertisers because it directly impacts the effectiveness of their campaigns.
If an ad is not viewable, it cannot influence users or drive desired actions (such as clicks or conversions).
Therefore, advertisers often aim to improve viewability to get more value from their ad spend.
Viewability Measurement:
Advertisers and publishers use various ad verification and viewability measurement tools to track viewability metrics.
These tools provide insights into which ads are viewable and which are not, helping advertisers optimise their campaigns.
9. What is the Role of Conversion Tracking in GDN Advertising?
Conversion tracking plays a crucial role in Google Display Network (GDN) advertising, just as it does in other digital advertising platforms. Its primary purpose is to measure and track the effectiveness of your GDN campaigns by monitoring specific actions or "conversions" that users take after interacting with your ads.
Here are the key roles and benefits of conversion tracking in GDN advertising:
- Measuring ROI
- Optimising Campaigns
- Understanding User Behavior
- Attribution Modeling
- Setting Performance Benchmarks
- Budget Allocation
- Automated Bidding
- Remarketing
- Tracking Different Conversion Actions
Conversion tracking in GDN advertising is essential for measuring performance, optimising campaigns, understanding user behavior, and making data-driven decisions to maximise the effectiveness and efficiency of your display advertising efforts.
It helps you allocate resources more effectively and achieve your desired advertising goals.
10. How Can You Ensure Compliance with Google's Policies and Guidelines in GDN Advertising?
Ensuring compliance with Google's policies and guidelines in Google Display Network (GDN) advertising is crucial to avoid ad disapprovals, account suspensions, and other negative consequences.
Here are steps you can take to ensure compliance:
- Familiarise Yourself with Google's Policies.
- Follow the Content Policies
- Adhere to Specific Ad Formats
- Use Safe and Appropriate Landing Pages
- Avoid Prohibited Content and Practices
Google has strict guidelines regarding prohibited content and practices, including but not limited to:
- Adult content
- Gambling
- Trademarks
- Misrepresentation
- Use Proper Targeting
- Monitor and Review Ad Campaigns
- Utilise Google's Ad Review Process
- Stay Informed
- Seek Guidance
- Report Violations
Compliance with Google's policies is essential for a successful and sustainable advertising campaign on the Google Display Network. Failure to comply with these policies can lead to ad disapprovals, account suspensions, and damage to your brand's reputation.
YouTube Ads Interview Questions and Answers

1. What are YouTube Ads, and What are the Different Ad Formats Available?
YouTube ads are a form of advertising that allows businesses and individuals to promote their products, services, or content on the YouTube platform.
These ads can appear before, during, or after YouTube videos, as well as in other places on the platform, such as in search results and on the YouTube homepage.
YouTube ads are a popular way for advertisers to reach a large and diverse audience, as YouTube is one of the most visited websites in the world and has billions of users.
There are several different ad formats available on YouTube, each with its characteristics and purposes:
Skippable Video Ads (TrueView Ads):
- These are the most common types of YouTube ads.
- Viewers have the option to skip the ad after the first 5 seconds.
- Advertisers are only charged when viewers watch 30 seconds of the ad (or the entire ad if it's shorter than 30 seconds) or engage with the ad, such as by clicking on a call-to-action (CTA) overlay.
Non-Skippable Video Ads:
- Viewers cannot skip these ads, and typically last for 15 seconds.
- They are designed for short, concise messages but can be perceived as intrusive by some users.
Bumper Ads:
- Bumper ads are short, non-skippable video ads that are limited to a maximum of 6 seconds in length.
- They are designed for brief, memorable messages and are often used to increase brand awareness.
Overlay Ads (Sponsored Cards):
- These are semi-transparent ads that appear as overlays on the lower portion of a video.
- They can include images, text, and CTA buttons.
- Viewers can click on these ads to get more information without leaving the video they're watching.
Display Ads:
- Display ads are shown alongside YouTube videos, typically on the right-hand side of the desktop site or below the video on mobile devices.
- They can include text, images, and sometimes video.
Discovery Ads (formerly In-Display Ads):
- These ads appear on the YouTube search results page and as related videos on the YouTube homepage.
- They consist of a thumbnail image and headline.
- Advertisers pay when viewers click on the ad to watch the video.
Masthead Ads:
- These are premium ads that appear at the top of the YouTube homepage for a specific period (usually 24 hours).
- They are typically used for major advertising campaigns and can have a significant reach.
Outstream Ads:
- These ads are designed for mobile devices and appear on partner websites and apps, not just on YouTube.
- They are usually displayed within articles and can be either skippable or non-skippable.
Sponsored Product Ads (Shopping Ads):
- These ads are used by e-commerce businesses to promote their products on YouTube.
- They appear in search results and related videos, showcasing products with images, prices, and CTA buttons.
Each of these ad formats serves different marketing objectives and can be tailored to suit specific campaign goals and budgets. Advertisers can use YouTube's advertising platform, Google Ads, to create and manage their YouTube ad campaigns.
2. Explain the Concept of TrueView In-stream Ads and How They Work
TrueView in-stream ads are a type of video advertising format offered by Google through its advertising platform, Google Ads. These ads are primarily used on YouTube, one of the largest video-sharing platforms on the internet.
They’re designed to provide a more engaging and user-friendly advertising experience for both viewers and advertisers by giving viewers control over the ads they watch.
Here's how TrueView in-stream ads work:
- Ad Placement: TrueView in-stream ads are played before, during, or after a YouTube video. They can also appear on websites and apps that are part of the Google Display Network.
- User Control: One of the key features of TrueView in-stream ads is that they are skippable. Viewers are typically given the option to skip the ad after watching it for five seconds.
- Ad Length: TrueView in-stream ads can vary in length, but they are often around 30 seconds. Advertisers can also create shorter or longer ads based on their goals and content.
- Targeting and Bidding: Advertisers can target their TrueView in-stream ads to specific demographics, interests, keywords, and more through Google Ads. They can also set their bidding strategy based on different goals, such as views or conversions.
- Cost Control: Since advertisers only pay when viewers engage with their ad by watching a particular portion of it or taking a specific action, TrueView in-stream ads offer more control over ad spend and return on investment.
- Engagement Features: TrueView in-stream ads can include various interactive elements, such as clickable call-to-action overlays, end screens, and companion banners, which provide viewers with additional information and opportunities to engage with the advertiser's content.
- Performance Metrics: Advertisers can track the performance of their TrueView in-stream ads using metrics like view rate (the percentage of viewers who watch at least 30 seconds of the ad), click-through rate (CTR), and conversion tracking to measure the impact of their campaigns.
- Ad Format Flexibility: TrueView in-stream ads can be used for various marketing objectives, including brand awareness, product promotion, lead generation, and more. Advertisers have the flexibility to tailor their ad creative to suit their specific goals.
TrueView in-stream ads on YouTube and the Google Display Network offer advertisers a cost-effective and user-friendly way to reach their target audience through video content.
3. What is the Difference Between TrueView In-Stream Ads and TrueView Discovery Ads?
TrueView in-stream ads and TrueView discovery ads are two different types of video advertising formats offered by Google through its advertising platform, Google Ads. While both formats are part of the TrueView advertising family and are designed for YouTube and the Google Display Network, they have distinct characteristics and serve different purposes.
Here are the key differences between TrueView in-stream ads and TrueView discovery ads:
| TrueView In-Stream Ads | TrueView Discovery Ads | |
| Ad Placement | These ads are played before, during, or after a YouTube video or on websites and apps within the Google Display Network. They typically appear as skippable video ads that viewers can skip after watching for five seconds. | TrueView discovery ads, formerly known as TrueView in-display ads, are displayed in YouTube search results next to related videos on YouTube watch pages and the YouTube homepage. They appear as thumbnail images and text, enticing viewers to click and watch the video. |
| Viewer Engagement | In-stream ads are video ads that viewers must watch before they can access the content they intended to watch. Viewers have the option to skip the ad after the first five seconds. Advertisers are charged when viewers watch at least 30 seconds of the ad or interact with it. | Discovery ads are displayed alongside other YouTube content, and viewers choose to engage with them by clicking on the thumbnail and title. They are taken to the advertiser's video-watch page. Advertisers are charged when viewers click on the ad thumbnail and start watching the video. |
| Ad Format | In-stream ads are video-centric. Advertisers create video content that plays as a skippable ad. The video content should be engaging and capture viewers' attention within the first few seconds to encourage them to watch more. | Discovery ads consist of a thumbnail image, headline, and brief text description. They are designed to blend in with the organic content on YouTube and rely on compelling thumbnails and titles to attract clicks. |
| Ad Creative | Advertisers have more control over the storytelling and content of in-stream ads, as they are creating a video that viewers will watch. They can use video to convey their message creatively. | Advertisers need to create an engaging thumbnail image and a compelling title since these elements are the primary factors that determine whether viewers click on the ad. |
| Viewer Intent | Viewers may not have initially intended to watch an ad but are required to do so before accessing their desired content. Advertisers aim to capture their attention quickly. | Viewers actively choose to engage with discovery ads by clicking on the thumbnail, indicating a higher level of interest in the content. |
TrueView in-stream ads are video ads that play before, during, or after video content. In contrast, TrueView discovery ads are displayed alongside other YouTube content and rely on clickable thumbnails and titles.
The choice between these formats depends on your advertising goals, budget, and the type of engagement you seek from viewers.
4. How Can Advertisers Target Their YouTube Ads to Specific Audiences?
Advertisers can target their YouTube ads to specific audiences using a variety of targeting options available through Google Ads.
These options allow advertisers to reach users based on demographics, interests, behaviors, and more.
Here's how advertisers can target their YouTube ads to specific audiences:
Demographic Targeting:
- Age: Advertisers can specify the age range of the audience they want to reach. For example, they can target users aged 18-34 or 35-55.
- Gender: Advertisers can target their ads to specific genders, such as male, female, or all genders.
Location Targeting:
- Geography: Advertisers can target users based on their location, including countries, regions, cities, and even specific radius targeting around a location.
Interest-Based Targeting:
- Affinity Audiences: These are broad, interest-based categories that target users with a demonstrated interest in specific topics or industries. For example, "Travel Buffs" or "Fitness Enthusiasts."
- In-Market Audiences: These target users who are actively researching or showing intent to purchase products or services in specific categories, such as "Home Improvement" or "Auto Dealerships."
- Custom Affinity Audiences: Advertisers can create custom affinity audiences based on specific interests, websites, or keywords related to their target audience.
- Life Events: Target users who are going through specific life events, such as getting married or moving to a new home.
Behavioural Targeting:
- Remarketing: Advertisers can show ads to users who have previously interacted with their website, YouTube channel, or mobile app. This helps in re-engaging potential customers.
- Custom Intent Audiences: Advertisers can create custom intent audiences based on keywords and URLs related to their products or services. This targets users actively searching for specific terms on Google.
- Customer Match: Advertisers can upload their customer lists to Google Ads and target ads to users on YouTube who match the uploaded email addresses.
Content Targeting:
- Placements: Advertisers can choose specific YouTube videos, channels, or websites where they want their ads to appear. This can be particularly useful for aligning ads with relevant content.
- Keywords: Advertisers can target their ads based on specific keywords related to the content users are searching for or watching on YouTube.
- Topics: Ads can be targeted to specific topics or categories on YouTube, such as "Technology" or "Travel."
Device and Platform Targeting:
Advertisers can choose to target users on specific devices, such as mobile devices, computers, or TVs. They can also target users on specific operating systems or apps.
Audience Exclusions:
Advertisers can exclude specific audiences to ensure their ads only appear to users who are part of their target audience.
Ad Scheduling:
Advertisers can specify when their ads should run, allowing them to target specific times of the day or days of the week when their audience is most active.
Budget and Bid Strategies.
5. What is the Significance of Ad Sequencing on YouTube, and How Can it Benefit Advertisers?
Ad sequencing on YouTube refers to a strategic approach to delivering a series of video ads to viewers in a specific order. The significance of ad sequencing on YouTube lies in its ability to benefit advertisers in several ways.
- Improved storytelling: Ad sequencing allows advertisers to tell a story or convey a message progressively over a series of video ads. This can help build a stronger emotional connection with the audience and keep them engaged over multiple touchpoints.
- Enhanced brand recall: By presenting a sequence of ads with a consistent message and theme, advertisers can reinforce their brand identity and make it more memorable for viewers.
- Increased engagement: Viewers are more likely to watch a series of ads that are linked by a compelling narrative. This can lead to higher engagement rates and a deeper level of interaction with the brand's content.
- Message reinforcement: Ad sequencing enables advertisers to reinforce key messages or product benefits across multiple videos, increasing the likelihood that viewers will remember and act upon the information presented.
- Better targeting options: YouTube offers sophisticated targeting capabilities, allowing advertisers to reach specific audience segments with each ad in the sequence. This ensures that the right message reaches the right people at the right time.
- Cross-device consistency: Ad sequencing can be designed to work seamlessly across different devices, ensuring a consistent user experience for viewers who switch between mobile, desktop, and smart TV screens.
- Ad frequency management: Advertisers can control the frequency at which viewers see each ad in the sequence, preventing overexposure and ad fatigue while maximising the impact of their campaign.
- Measurable results: YouTube provides detailed analytics and reporting tools, allowing advertisers to track the performance of each ad in the sequence and make data-driven adjustments to optimise their campaigns.
- Increased conversions: Ad sequencing can guide viewers through a customer journey, from awareness to consideration and ultimately to conversion. By tailoring the messaging to each stage, advertisers can drive more conversions and sales.
- Competitive advantage: Ad sequencing is a relatively advanced advertising technique, and advertisers who use it effectively can gain a competitive edge by delivering a more compelling and memorable brand experience.
To benefit from ad sequencing on YouTube, advertisers should:
- Plan a cohesive narrative: Create a clear and engaging story or message that can be effectively divided into a sequence of videos.
- Define audience segments: Identify specific audience segments and tailor each ad in the sequence to address their unique interests and needs.
- Set clear objectives: Determine the goals of each ad in the sequence, whether it's raising awareness, driving consideration, or encouraging conversion.
- Monitor and optimise: Continuously analyse the performance of each ad in the sequence, adjusting as needed to improve results and ROI.
6. Explain How Auction Bidding Works for YouTube Ads
YouTube advertising primarily utilises an auction-based system called "Google Ads" for advertisers to bid on ad placements.
While I can provide a general overview of how auction bidding works for YouTube ads, please note that there may have been updates or changes to the platform since then.
Here's a basic explanation of how YouTube ad auction bidding typically works:
- Ad Campaign Setup: Advertisers start by setting up a Google Ads campaign and specifying their advertising goals, target audience, ad format preferences (e.g., TrueView, skippable ads, non-skippable ads, etc.), budget, and bid strategy.
- Ad Group and Ad Creation: Within the campaign, advertisers create ad groups that contain one or more ads. Advertisers can create various ad creatives (videos) to test different messaging or visuals.
- Targeting: Advertisers can define their target audience by factors such as demographics, interests, location, and more. This helps narrow down who will see their ads.
- Bidding Strategy: Advertisers choose their bidding strategy. Google Ads offers several bidding options.
- CPV (Cost Per View): Advertisers bid on the cost they're willing to pay for a view of their video ad. You pay when a viewer watches 30 seconds of your video or interacts with it, whichever comes first.
- CPM (Cost Per Thousand Impressions): Advertisers bid on the cost for every 1,000 times their ad is shown.
- Target CPA (Cost Per Acquisition): Advertisers set a target cost per conversion, and Google's automated bidding system adjusts the bid to meet that goal.
- Ad Auction: When a user visits YouTube and starts watching a video, YouTube's ad auction begins. The auction considers various factors to determine which ad to show, including the advertiser's bid, ad quality, and relevance to the viewer.
- Ad Rank: Advertisers' bids, ad quality, and other factors contribute to their ad rank. Ad rank is a measure of how competitive an ad is in the auction. Higher ad ranks increase the likelihood of winning the auction and having the ad displayed.
- Ad Delivery: If an advertiser's ad wins the auction, it is shown to the viewer. The actual cost paid by the advertiser depends on the competition in the auction and the next highest competing bid.
- Ad Reporting: Advertisers can access detailed reporting and analytics to track the performance of their ads, including views, click-through rates (CTR), and conversion data.
- Optimisation: Based on the performance data, advertisers can optimise their campaigns by adjusting bidding strategies, ad creatives, targeting parameters, and budgets to achieve their desired goals.
7. What is the YouTube Masthead Ad Format, and Where Does it Appear on the Platform?
YouTube Masthead ad format is a prominent and noticeable ad placement on the YouTube platform. It's a premium advertising format that allows advertisers to showcase their video content to a massive audience.
- Placement: The YouTube Masthead ad appears prominently at the top of the YouTube homepage on both desktop and mobile devices. It's one of the first things users see when they visit the YouTube website or app, making it a high-impact ad format.
- Video or Creative: The Masthead ad can be a video ad or an image-based creative. If it's a video ad, it typically auto-plays without sound when the user lands on the homepage. Users can click on the ad to watch the full video with sound.
- Availability: The Masthead ad is available on a reservation basis, meaning advertisers need to book this premium ad slot in advance. It's often used for significant product launches, movie releases, or other high-profile campaigns.
- Duration: Typically, the Masthead ad appears for 24 hours. Advertisers can choose specific start and end times for their campaigns.
- Targeting: Advertisers can target their Masthead ads based on factors like geography, demographics, interests, and more to reach their desired audience.
- Engagement: Users can interact with the Masthead ad by clicking on it to watch the full video or visiting the advertiser's website.
8. Explain What Targeting by Custom Intent Audiences Means on YouTube
Targeting by custom intent audiences on YouTube is a feature that allows advertisers to reach a specific audience based on their demonstrated interests and intent as inferred from their online behaviour.
It enables advertisers to deliver their video ads to users who have shown an interest in products, services, or topics related to their offerings.
Here's a more detailed explanation of targeting by custom intent audiences on YouTube:
- Custom Intent Audiences: Custom intent audiences are user segments created by advertisers. These segments are defined by specific keywords and URLs related to the products or services they are promoting. Advertisers can create custom intent audiences to match their ideal customer profiles or to target users actively searching for or consuming content related to their offerings.
- Keywords and URLs: Advertisers can input a list of relevant keywords and URLs into the custom intent audience targeting settings. These keywords and URLs should be directly related to the products or services they want to promote. YouTube then uses this information to identify users who have recently searched for these keywords or interacted with content on those URLs.
- User Intent: Custom intent audiences are influential because they focus on user intent. They target individuals who have already shown an interest in specific topics or products, making them more likely to engage with relevant ads.
- In-Market vs. Custom Intent Audiences: While in-market audiences target users actively researching or considering a purchase, custom intent audiences go a step further by allowing advertisers to define their keywords and URLs, giving them more control over targeting.
- Ad Formats: Custom intent audience targeting can be used with various ad formats on YouTube, including TrueView video ads, display ads, and discovery ads. This flexibility allows advertisers to choose the ad format that best suits their campaign objectives.
- Campaign Goals: Custom intent audience targeting can be effective for various campaign goals, such as driving website visits, increasing brand awareness, or generating leads and conversions.
- Performance Tracking: YouTube provides advertisers with analytics and reporting tools to track the performance of their custom intent audience campaigns. This data helps advertisers assess the effectiveness of their targeting and make necessary adjustments.
- Continuous Optimisation: Advertisers should continually refine and optimise their custom intent audience targeting based on performance data. This may involve adjusting keywords and URLs, refining ad creatives, or modifying bidding strategies.
9. What is YouTube's policy on Ad Content, and Why is it Important for Advertisers to Adhere to these Policies?
YouTube has a set of policies and guidelines regarding ad content that advertisers must adhere to when running ads on the platform.
These policies are in place to maintain a safe and positive user experience on YouTube, protect viewers from harmful or inappropriate content, and ensure that advertisers are promoting content that aligns with community standards.
Here are some key aspects of YouTube's ad content policies and why advertisers need to adhere to them:
- Content Guidelines: YouTube's ad content policies cover various aspects of ad content, including but not limited to.
- Prohibited Content: Advertisers are not allowed to promote content that is harmful, deceptive, or illegal, including hate speech, violence, misleading claims, and illegal products or services.
- Copyright and Trademark: Advertisers must have the necessary rights and permissions to use copyrighted or trademarked materials in their ads.
- Sensitive Content: Some content, such as alcohol, gambling, and healthcare-related ads, may be subject to additional restrictions and requirements.
- Children's Privacy: Advertisers must comply with laws and regulations regarding the collection of data from children and must specify if their ad content is directed at children.
- Ad Review Process: YouTube has a review process in place to ensure that ads comply with its policies. Advertisers submit their ads for review, and YouTube's team assesses whether the ad content adheres to the guidelines. This process helps prevent inappropriate or harmful content from being promoted on the platform.
- Placement: YouTube also has policies regarding where ads can appear. Advertisers can choose the types of content and channels where their ads are shown, and they can exclude specific categories or content types if they wish to do so.
- User Experience: Adherence to YouTube's policies helps maintain a positive user experience. When viewers encounter ads that are relevant, safe, and respectful, they are more likely to engage with the content and the brand being advertised.
- Brand Reputation: Advertisers are responsible for their brand's reputation. Associating with harmful or inappropriate content can damage a brand's image and credibility.
- Penalties for Non-Compliance: Advertisers who violate YouTube's ad content policies may face consequences, such as ad removal, suspension of ad accounts, or other actions. Non-compliance can also result in a negative impact on the advertiser's ad campaign performance.
- User Trust: Advertisers should aim to build trust with their audience. Ensuring that ad content is accurate, safe, and compliant with community guidelines helps establish trust with viewers.
- Legal Compliance: Advertisers must also adhere to legal and regulatory requirements in their advertising, such as consumer protection laws, data privacy regulations, and advertising standards set by relevant authorities.
It's essential for advertisers to thoroughly review and understand YouTube's ad content policies and ensure that their ad campaigns comply with these guidelines.
- Avoid ad disruptions and penalties.
- Build a positive brand image and reputation.
- Reach a larger and more engaged audience on YouTube.
- Create a safer and more enjoyable user experience for viewers.
- As YouTube's policies and guidelines may change over time, advertisers should regularly check YouTube's official advertising resources and seek guidance from YouTube's advertising support team to stay up to date with the latest policies and requirements.
10. Explain the Concept of YouTube Remarketing and How it can be Used Effectively in Advertising Campaigns
YouTube remarketing is a digital advertising strategy that allows advertisers to target individuals who have previously interacted with their YouTube channel, videos, or website.
It is a powerful technique to re-engage users who have already shown some level of interest in your brand or content.
Remarketing helps keep your brand top-of-mind and encourages users to take desired actions, such as making a purchase, signing up for a newsletter, or simply continuing to engage with your content.
Here's how YouTube remarketing works and how it can be used effectively in advertising campaigns:
- Tracking User Interactions: To initiate a YouTube remarketing campaign, you first need to set up tracking mechanisms, such as Google Analytics and the YouTube pixel, on your website or YouTube channel. These tools monitor user interactions, like video views, website visits, and conversions.
- Building Audiences: After tracking user interactions, you can create custom audiences based on specific criteria.
Here are a few examples:
- All Visitors: Target all users who have visited your website or interacted with your YouTube channel.
- Video Viewers: Target users who have watched a certain percentage of your videos or specific videos on your channel.
- Website Visitors: Target users who have visited specific pages or taken specific actions on your website, like viewing a product page or adding items to a cart.
- Creating Remarketing Lists: Once you have defined your custom audiences, you can create remarketing lists. These lists segment users based on their behaviour, making it easier to tailor your ad content to their interests and actions.
Benefits of YouTube Remarketing:
- Higher Conversion Rates: Remarketing targets users who are already familiar with your brand or products, increasing the likelihood of conversions.
- Cost-Effective: Since you're targeting a warm audience, remarketing campaigns often have lower costs per conversion compared to cold audiences.
- Personalisation: You can tailor your ads to specific audience segments, delivering content that aligns with their interests and behaviours.
- Brand Reinforcement: Remarketing keeps your brand in front of users, reinforcing brand awareness and trust.
- Cross-Device Targeting: YouTube remarketing can reach users on various devices, ensuring a consistent brand experience.
11. What is the YouTube Partner Program, and How Does It Relate to Advertising on YouTube?
The YouTube Partner Program is a program offered by YouTube that allows content creators, often referred to as YouTubers or YouTuber channels, to monetise their videos by earning revenue from advertising displayed on their content.
Here's how the YouTube Partner Program relates to advertising on YouTube:
Eligibility:
To join the YouTube Partner Program, creators need to meet specific eligibility requirements set by YouTube.
These requirements typically include having at least 1,000 subscribers and 4,000 watch hours on their channel within the past 12 months. Eligibility criteria may vary over time, and YouTube may update them.
Monetization:
Once a channel is accepted into the YPP, creators can monetise their videos by allowing YouTube to display ads before, during, or after their content.
Creators earn a share of the revenue generated from these ads. Advertisements can take various forms, such as display ads, skippable video ads (TrueView ads), non-skippable video ads, and more.
Ad Revenue Sharing:
YouTube shares a portion of the revenue generated from ads with the content creator. The exact revenue share varies and depends on several factors, including the type of ad and the location of the viewers.
In general, creators receive a percentage of the advertising revenue, typically around 55-45, with 55% going to the creator and 45% to YouTube.
Ad Types:
YouTube offers various ad formats that advertisers can use to promote their products or services on the platform. These include:
- TrueView Ads: These are skippable video ads that viewers can skip after a few seconds. Creators earn revenue when viewers watch a significant portion of these ads.
- Non-Skippable Ads: These are short video ads that viewers cannot skip. Creators earn revenue based on ad impressions.
- Display Ads: These are shown alongside the video content. Creators earn revenue based on impressions and clicks.
- Overlay Ads: These are semi-transparent ads that appear on the lower part of a video. Creators earn revenue based on clicks.
- Bumper Ads: These are short, non-skippable ads that are typically six seconds long. Creators earn revenue based on impressions.
Revenue Payouts:
YouTube typically pays creators their share of ad revenue monthly, provided they meet the minimum payout threshold.
Creators can receive their earnings through various payment methods, including bank transfers, checks, or AdSense accounts.
12. How Can Advertisers Measure the Success of Their YouTube Ad Campaigns, and What Key Performance Metrics Should They Monitor?
Advertisers can measure the success of their YouTube ad campaigns by monitoring various key performance metrics that provide insights into how their ads are performing and how well they are achieving their advertising goals.
Here are some essential metrics to monitor:
- View Count
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- View-Through Rate (VTR)
- Conversion Rate
- Cost-Per-Click (CPC) or Cost-Per-View (CPV)
- Return on Investment (ROI)
- Engagement Metrics
- Audience Retention
- Ad Placement Metrics
- Viewability
- Brand Lift
- Ad Frequency
- Geographic and Demographic Data
- Watch Time
- Ad Recall and Awareness
Advertisers should set clear objectives and goals for their YouTube ad campaigns before launch and then regularly analyse these metrics to assess performance.
It's essential to use a combination of these metrics to gain a comprehensive understanding of the campaign's success and make data-driven optimisations to improve results over time.
Google Shopping Ads Interview Questions and Answers
1. What are Google Shopping Ads, and how do they differ from traditional text ads?
Google Shopping Ads, also known as Product Listing Ads (PLAs), are a type of advertising format offered by Google as part of its advertising platform, Google Ads.
These ads are designed specifically for e-commerce businesses to promote their products and reach potential customers when they are actively searching for products to buy on Google's search engine or other Google-owned platforms like Google Shopping.
Here are the key features and differences between Google Shopping Ads and traditional text ads:
| Google Shopping Ads | Traditional Text Ads | |
| Visual Representation | These ads display product images, along with the product title, price, and the name of the retailer. Users can see a picture of the product before clicking on the ad, which provides a more visual and immediate understanding of what is being offered. | Text ads consist of headlines, description lines, and URL links. They do not include images or specific product information, relying solely on text to convey the message. |
| Product Listings | These ads are linked directly to a product feed provided by the advertiser, which includes details such as product images, titles, descriptions, prices, and availability. Google automatically matches user queries with relevant products from the advertiser's feed. | Text ads are more generic and rely on keywords and ad copy to match with user queries. They don't have a direct connection to specific product listings. |
| Keyword Targeting | While keywords can be used to influence which searches trigger your Shopping Ads, the primary targeting is based on the product data provided in your feed. Google uses this data to determine when to show your ads. | These ads primarily rely on keyword targeting. Advertisers bid on specific keywords, and their ads appear when users search for those keywords. |
| Cost Structure | Typically, advertisers pay for clicks (Cost Per Click or CPC) on their Shopping Ads. The competition for ad placements can affect the cost. | Advertisers also pay for clicks with text ads, but the cost can vary based on keyword competitiveness, ad quality, and other factors. |
| Ad Auctions | Advertisers in Google Shopping compete for ad placements based on the quality and relevance of their product data and bids. Google uses a combination of factors to determine which ads to show for a given search query. | Advertisers in text ad auctions compete primarily based on keyword bids, ad quality scores, and other factors like ad extensions. |
| Ad Placement | These ads typically appear at the top of Google's search results or in the Google Shopping tab, often in a prominent position with images. | Text ads can appear at the top or bottom of search results and on various Google partner sites within the Google Display Network. |
2. Explain the Key Components of a Google Shopping Ad
Google Shopping ads are a type of online advertising format offered by Google that allows e-commerce businesses to showcase their products directly within Google's search results.
These ads are designed to help businesses promote their products and drive relevant traffic to their online stores.
These are the key components of a Google Shopping ad:
- Product Image: The product image is one of the most crucial components of a Google Shopping ad. It's a high-quality image of the product being advertised. Google typically requires product images to meet specific size and quality standards to ensure a visually appealing and informative experience for users.
- Product Title: The product title is a concise and descriptive headline that provides information about the product. It should accurately represent the product and contain relevant keywords that potential customers might use when searching for similar products.
- Price: The price of the product is prominently displayed in the ad. This helps potential customers quickly assess whether the product fits within their budget.
- Store Name: The store name is the name of the retailer or e-commerce store where the product is available for purchase. It helps establish brand recognition and trust with potential customers.
- Product Description: A brief product description provides additional details about the product. While it may not be as prominent as the title, it can still influence a user's decision to click on the ad and learn more about the product.
- Product Ratings and Reviews: Google may display the average product rating and the number of reviews received by the product. Positive ratings and reviews can boost a user's confidence in the product and the seller.
- Promotions and Discounts: If applicable, Google Shopping ads may include information about special promotions, discounts, or offers related to the product. This can make the ad more appealing to potential customers.
- Shopping Ad Extensions: Google allows advertisers to include various ad extensions, such as seller ratings, free shipping, and additional product details. These extensions enhance the ad's visibility and provide more information to users.
- Shopping Campaign Settings: Advertisers set campaign parameters, including budget, bidding strategy, location targeting, and more. These settings help control when and where the ads appear and how they are optimised for performance.
- Product Feed: Behind the scenes, advertisers maintain a product feed, which is a data file containing detailed information about their products. This feed includes data like product IDs, prices, availability, and other product attributes. Google uses this feed to create and display Shopping ads.
- Ad Group Structure: Google Shopping campaigns are organized into ad groups, each containing a subset of products from the product feed. Advertisers can customise bids and settings for each ad group to optimise performance.
- Keywords (optional): While not as prominent as in traditional text ads, keywords can still play a role in Google Shopping campaigns. Advertisers can use negative keywords to exclude irrelevant searches and ensure their ads are shown to the most relevant audience.
3. How Do You Optimise Product Titles and Descriptions for Google Shopping Ads?
Optimising product titles and descriptions for Google Shopping Ads is crucial for improving the visibility and performance of your ads.
Here are some best practices to help you optimise your product titles and descriptions effectively:
- Use Descriptive and Relevant Titles
- Include High-Value Keywords
- Follow Google's Guidelines
- Use Unique Product Identifiers
- Highlight Product Differentiators
- Optimise Descriptions
- High-Quality Images
- Regularly Review and Update
- Be Transparent
- Localize for Different Markets
- Use Negative Keywords
- Structured Data Markup
- A/B Testing
Remember that optimisation is an ongoing process, and what works for one product or campaign may not work for another. Regularly analysing data and adjusting your strategies based on performance metrics is essential for long-term success with Google Shopping Ads.
4. Can you Explain the Concept of Product Listing Ads (PLAs) and How They Work?
Product Listing Ads (PLAs) are a type of online advertising format primarily used by e-commerce businesses to promote their products on search engine result pages, particularly on Google. They are a highly effective way for businesses to showcase their products to potential customers who are actively searching for products online.
Here's how PLAs work and the key concepts associated with them:
- Product Feed: PLAs begin with a product feed. This is a structured data file that contains information about the products you want to advertise, such as product titles, descriptions, prices, images, and product IDs.
- Campaign Creation: To create a PLA campaign, advertisers use advertising platforms like Google Ads. Within the campaign, advertisers set their budget, bidding strategy, and targeting parameters.
- Ad Creation: Instead of writing traditional text ads, advertisers create PLAs by specifying which products they want to promote from their product feed. PLAs typically include an image of the product, the product's title, the price, and the store's name.
- Keyword Targeting: Unlike traditional text ads where keywords trigger the ad display, PLAs rely on product attributes and data from the product feed. Google uses a combination of product data and user search queries to determine when and where to display PLAs.
- Auction and Display: When a user enters a relevant search query, the advertising platform (e.g., Google Ads) enters PLAs into an auction along with other advertisers' ads. The platform then determines the ad's position based on factors like bid amount, ad quality, and relevance to the user's query.
- Display on Search Results: If your PLA wins the auction, it is displayed prominently on the search engine results page (SERP) when a user searches for a related product. The PLA typically appears at the top of the page or in a sidebar, showcasing the product image, price, and other details.
- Clicks and Conversions: Users who click on the PLA are directed to the product's landing page on the advertiser's website. Advertisers pay for clicks on the PLA, making PLAs a cost-per-click (CPC) advertising model. The ultimate goal is to convert these clicks into sales.
- Performance Monitoring: Advertisers can track the performance of their PLAs through analytics provided by the advertising platform. This data helps them measure the ROI of their campaigns and make adjustments to improve results.
Key Benefits of PLAs:
- Visual Appeal: PLAs feature product images, making them more visually appealing and engaging for users.
- Relevance: PLAs are highly relevant to user queries, as they are triggered based on the product data in the feed.
- Targeted Advertising: Advertisers can segment products and target specific audiences based on attributes, allowing for precise ad targeting.
- Competitive Advantage: PLAs often appear at the top of search results, giving advertisers a competitive edge.
5. How Do You Set Up a Google Merchant Center Account, and Why is It Necessary for Running Shopping Ads?.
Setting up a Google Merchant Center account is a crucial step in running Shopping Ads on Google. It allows you to upload, manage, and promote your product listings on Google Shopping.
Here's how to set up a Google Merchant Center account and why it's necessary for running Shopping Ads:
- How to Set Up a Google Merchant Center Account.
- Visit the Google Merchant Center website.
- Sign in or create a Google Account.
- Provide basic business information.
- Verify your website.
- Set up tax and shipping information.
- Create your data feed.
- Upload your data feed.
- Submit your products for review.
- Wait for approval.
Why Google Merchant Center is Necessary for Shopping Ads:
- Product Listings: Google Merchant Center serves as the repository for your product listings. To run Shopping Ads, you need a central place to store and manage your product data. Merchant Center helps you organize and maintain this information.
- Data Quality: Google uses the data you provide in your Merchant Center account to create and display Shopping Ads. Ensuring that your product data is accurate, up-to-date, and compliant with Google's policies is essential for the success of your Shopping Ads campaigns.
- Ad Creation: When you create Shopping Ads campaigns in Google Ads, you link them to your Merchant Center account. This connection allows you to use your product data to create ads that feature product images, titles, prices, and more.
- Targeting and Optimisation: Merchant Center data helps Google understand your products, making it easier to match them with relevant search queries. This targeting and optimisation are crucial for driving traffic and conversions through your Shopping Ads.
6. What are the Different Bidding Strategies Available for Google Shopping Ads, and When Might You Use Each One?
Google Shopping Ads offers several bidding strategies to help advertisers optimise their campaigns. The choice of bidding strategy depends on your advertising goals and the level of control you want over your campaign's performance.
Here are some of the different bidding strategies available for Google Shopping Ads and when you might use each one:
- Manual CPC (Cost-Per-Click) Bidding: Use manual CPC bidding when you want complete control over your bids and are comfortable adjusting them manually. This strategy allows you to set individual bids for each product group within your campaign.
- Enhanced CPC (eCPC): Enhanced CPC is a good choice when you want Google to adjust your bids to maximise conversions automatically. It's ideal if your primary goal is to increase conversions while maintaining manual control over some bids.
- Target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend): Use Target ROAS when you want to optimise your campaign for a specific return on ad spend. This strategy is suitable for advertisers with a clear understanding of their desired ROI and historical conversion data.
- Maximise Clicks: Maximise Clicks is a bidding strategy for maximizing the number of clicks within your budget. It's a good option when your primary goal is to drive traffic to your website, and you need specific conversion goals.
- Maximise Conversions: Maximise Conversions is suitable when your primary goal is to get the most conversions within your budget. Google will automatically adjust your bids to help you achieve this goal.
- Target Impression Share: If your main objective is to ensure your ads appear at the top of search results or on a specific percentage of eligible impressions, you can use this strategy. It's helpful in increasing brand visibility.
- Target Search Page Location: This strategy is similar to Target Impression Share but focuses specifically on bidding to appear at the top of the search results or on the first page. It's helpful in improving ad visibility.
- Maximise Conversion Value: Use Maximise Conversion Value when your primary goal is to get the most value (revenue) from your conversions. It's a strategy for optimising the total value generated by your campaign.
- Target Outranking Share: If you want to consistently outrank a specific competitor's ads in the search results, you can use this strategy. It helps you automatically bid to achieve a higher ad position than a specified competitor.
- Portfolio Bidding: Portfolio Bidding is useful when you're managing multiple campaigns and want to apply a single bidding strategy across all of them. It allows you to set a shared bidding strategy at the campaign or ad group level.
7. Describe the Process of Setting up a Google Shopping Campaign from Start to Finish.
Step 1: Prepare Your Website and Product Data
Before you start your campaign, you need to ensure that your website is ready and you have product data in a compatible format. This includes:
- Website Compliance: Ensure that your website complies with Google's policies, including product information and checkout process. Your website should also be mobile-friendly.
- Product Data Feed: Create a product data feed in a supported format like XML or CSV. This feed should contain detailed information about your products, including title, description, price, availability, and more. Make sure it's regularly updated to reflect current inventory.
- Merchant Center Account: Sign up for a Google Merchant Center account if you still need to get one. This is where you'll upload and manage your product data feed.
Step 2: Set Up Google Ads Account
If you don't have a Google Ads account, you'll need to create one. If you already have an account, you can skip this step.
Step 3: Link Google Ads and Merchant Center Accounts
To connect your Google Ads and Merchant Center accounts:
a. Sign in to your Google Ads account.
b. Click on "Tools & Settings" and select "Linked accounts."
c. Click on "Google Merchant Center" and follow the prompts to link your accounts.
Step 4: Create a Google Shopping Campaign
Now, you're ready to set up your Google Shopping campaign:
a. In your Google Ads account, click on "Campaigns" and then the "+ New Campaign" button.
b. Select "Shopping" as the campaign type.
c. Choose your campaign subtype, such as "Sales" or "Leads." For most e-commerce businesses, "Sales" is the appropriate choice.
d. Configure your campaign settings, including budget, bidding strategy, location targeting, and other campaign-specific settings.
Step 5: Create Ad Groups
Within your Google Shopping campaign, you'll create ad groups to organize your products and set specific bids and priorities. Each ad group can have its bidding strategy.
a. Click on your newly created Shopping campaign.
b. Click on the "+ Ad Group" button to add ad groups.
c. Name your ad groups and set a default bid.
Step 6: Set Up Product Groups
Product groups allow you to organise your products within ad groups and set individual bids for each group based on attributes like product category, brand, or custom labels.
a. Click on an ad group to open it.
b. Click on the "+ Product group" button.
c. Choose how you want to subdivide your products, such as by product category, custom labels, or item IDs.
d. Set bids for each product group or subdivide further to create more specific groups.
Step 7: Create Shopping Ads
Google will automatically generate Shopping ads based on the product data you've provided. However, you can optimise your product feed for better ad performance.
Step 8: Review and Launch
Before launching your campaign, review all settings, including budget, targeting, and bidding. Make sure your product data feed in the Merchant Center is up-to-date and accurate.
Once you've reviewed everything and are satisfied with your settings, you can launch your Google Shopping campaign.
Step 9: Monitor and Optimise
After launching your campaign, ongoing monitoring and optimisation are essential. Analyse performance metrics, adjust bids, add negative keywords, and make other optimisations to improve your campaign's efficiency and ROI.
8. How Can You Measure the Performance of your Google Shopping Ads campaigns? What Key Metrics Should You Track?
Measuring the performance of your Google Shopping Ads campaigns is crucial for optimising your advertising strategy and maximising your return on investment (ROI).
Here are some of the most important ones:
- Click-Through Rate (CTR)
- Conversion Rate
- Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
- Cost-per-click (CPC)
- Average Order Value (AOV)
- Impression Share
- Quality Score
- Ad Position
- Click-Through Conversion Rate (CTR CVR)
- Click Share
- Product-Level Performance
- Mobile vs. Desktop Performance
- Geographic Performance
- Search Query Data
- Shopping Ad Benchmark Data
- Return on Investment (ROI) or Profit Margin
By tracking these key metrics, you can gain a comprehensive understanding of your Google Shopping Ads campaign's performance and make data-driven decisions to optimise your strategy for better results.
9. How do You Ensure That Your Google Shopping Ads are Compliant with Google's Policies and Guidelines?
Ensuring that your Google Shopping Ads are compliant with Google's policies and guidelines is crucial to avoid ad disapproval or account suspension.
Google has specific policies in place to maintain the quality and relevance of the ads displayed to users.
Here are some steps to help you ensure compliance:
- Read and Understand Google's Policies
- Use High-Quality Product Data
- Follow Google's Data Feed Specifications
- Use Unique Product Identifiers
- Maintain Pricing and Availability
- Create High-Quality Landing Pages
- Avoid Restricted Content
- Monitor and Review Your Ads
- Keep Abreast of Policy Updates
- Seek Google's Support
- Use Negative Keywords
- Set Up Conversion Tracking
By following these steps and staying vigilant, you can maintain compliance with Google's policies and guidelines, which will help ensure the success and longevity of your Google Shopping Ads campaigns.
Google Remarketing Ads Interview Questions and Answers
1. What is Google Remarketing, and How Does It Work?
Google Remarketing, also known as Google AdWords Remarketing, is a digital advertising strategy offered by Google Ads (formerly known as Google AdWords) that allows advertisers to re-engage with website visitors who have previously interacted with their site or app.

It's a powerful tool for reaching out to users who have shown interest in your products or services but have yet to convert (e.g., make a purchase, sign up, or complete another desired action) during their initial visit.
Here's how Google Remarketing works:
- Tagging Your Website: To initiate remarketing campaigns, you need to add a small piece of code called a "remarketing tag" to your website or app. This tag tracks user behaviour, such as pages visited, products viewed, and actions taken.
- Building Audiences: After installing the remarketing tag, you can create custom audiences based on specific criteria. For example, you can create an audience of users who visited a particular product page but didn't make a purchase. Google Ads provides various targeting options, allowing you to create highly segmented audiences.
- Setting Up Campaigns: Once you have defined your audiences, you can create remarketing campaigns within Google Ads. These campaigns can be display ads, text ads, or video ads that will be shown to users in your remarketing lists as they browse other websites, apps, or platforms within the Google Display Network, YouTube, or even in Google Search (if you're using remarketing lists for search ads).
- Ad Personalisation: You can tailor your remarketing ads to be highly relevant to the specific audience segments you've created. For example, if a user looks at a particular product, you can display ads featuring that product to encourage them to come back and complete a purchase.
- Bidding and Budgeting: You can set your bidding strategy and budget for your remarketing campaigns. Google Ads provides various bidding options, including manual bidding, automated bidding, and target ROAS (Return on Ad Spend) to optimise your ad placements.
- Ad Display: When users in your remarketing lists visit other websites or use apps within the Google network, Google's ad-serving technology displays your remarketing ads to them. These ads can appear as banner ads, text ads, video ads, or interactive ads, depending on your campaign settings and the platform being used.
- Conversion Tracking: To measure the effectiveness of your remarketing campaigns, it's essential to set up conversion tracking. This allows you to see whether users who clicked on your remarketing ads completed the desired actions on your site, such as making a purchase or filling out a contact form.
- Optimisation: Based on the performance data you gather, you can continually refine and optimise your remarketing campaigns by adjusting ad creatives, bids, targeting options, and audience segmentation to improve conversion rates and return on investment (ROI).
Google Remarketing helps businesses reconnect with users who have already expressed interest in their products or services, making it a valuable tool for increasing brand visibility, driving conversions, and maximizing the impact of your online advertising efforts.
2. Explain the Difference Between Standard Google Ads Campaigns and Google Remarketing campaigns.
Google Ads campaigns and Google Remarketing campaigns are two distinct types of advertising strategies offered by Google.
Here’s an explanation of the key differences between them:
| Google Ads Campaigns | Google Remarketing Campaigns | |
| Audience Targeting | In standard Google Ads campaigns (formerly known as Google AdWords), you create ads and target specific keywords, demographics, interests, and behaviours. You aim to reach users who are actively searching for products or services related to your keywords. | Remarketing campaigns, on the other hand, target users who have previously interacted with your website or mobile app. These users have already shown interest in your products or services. Remarketing allows you to re-engage them with customized ads based on their past actions on your site. |
| Ad Content | You design ads from scratch to capture the attention of potential customers. These ads can be text-based, image-based, video ads, or a combination of these formats. | Remarketing campaigns use ad content tailored to the specific audience's past behaviour. For example, if a user visited a product page on your website but didn't make a purchase, your remarketing ad might showcase the same product to remind them. |
| Conversion Intent | Standard Google Ads campaigns primarily target users who are in the research or buying phase and actively searching for information or products. These users may or may have yet to interact with your brand. | Remarketing campaigns focus on users who have already shown interest in your brand or products. They are further down the conversion funnel and are more likely to convert since they are already familiar with your brand. |
| Campaign Goals | Common goals for standard Google Ads campaigns include driving website traffic, generating leads, increasing sales, or promoting brand awareness. | Remarketing campaigns typically aim to increase conversion rates, reduce cart abandonment, and re-engage past visitors to boost sales and ROI. |
| Budget Allocation | You allocate your budget to reach a broad audience based on your chosen targeting criteria and keywords. | Remarketing campaigns often have a more specific and narrower audience, so that budget allocation may be different. You might allocate a portion of your budget specifically for remarketing efforts to maximise conversions among past visitors. |
| Ad Placement | Your standard ads can appear on Google search results, the Google Display Network (GDN), YouTube, and partner websites based on your targeting settings. | Remarketing ads can be displayed on the GDN, YouTube, and other Google-affiliated sites, but they primarily target users who have previously interacted with your site. |
3. What are the Primary Goals of Using Google Remarketing Ads in a Digital Marketing Strategy?
Google Remarketing Ads, also known as Google Remarketing or Google Display Remarketing, are a powerful tool in digital marketing strategies.
The primary goals of using Google Remarketing Ads are to:
- Increase Conversions
- Enhance Brand Awareness
- Targeted Advertising
- Cart Abandonment Recovery
- Cross-Sell and Up-Sell
- Improve ROI
- Customization and Personalization
- Ad Frequency Control
- Measure and Optimise
- Re-engage Lapsed Customers
- Mobile and Cross-Device Targeting
Google Remarketing Ads are a valuable component of a digital marketing strategy because they help re-engage past visitors, increase conversions, and provide a cost-effective way to target a specific audience with personalized messaging.
By leveraging the power of remarketing, businesses can maximise their marketing efforts and achieve better results.
4. Can you describe the different types of audiences you can target with Google Remarketing Ads?
Google Remarketing Ads allow advertisers to target specific audiences based on their previous interactions with a website or app. These audiences can be segmented in various ways to reach potential customers with tailored ads.
Here are the different types of audiences you can target with Google Remarketing Ads:
- Standard Remarketing: This type of remarketing targets users who have previously visited your website or app. Advertisers can show them ads as they browse other websites or use other apps across the Google Display Network.
- Dynamic Remarketing: Dynamic remarketing takes standard remarketing a step further by showing users specific products or services they viewed on your website. These ads can include product images, descriptions, and prices. It's particularly effective for e-commerce websites.
- Remarketing Lists for Search Ads (RLSA): RLSA allows advertisers to customize their search ads for users who have already visited their website. It allows for more granular bidding and ad customization to re-engage potential customers who are actively searching for related keywords on Google.
- Remarketing for Mobile Apps: This type of remarketing targets users who have interacted with your mobile app but still need to complete a desired action, such as making a purchase. You can encourage app installations or in-app actions with these ads.
- Video Remarketing: If you have a YouTube channel or use video ads, you can target users who have interacted with your videos or channel. This can include users who watched your videos or subscribed to your channel.
- Customer List Remarketing: Advertisers can upload customer lists (email addresses, phone numbers, etc.) to Google Ads, allowing them to target specific individuals or segments with tailored ads. This can be useful for re-engaging previous customers or promoting loyalty programs.
- Similar Audiences: Google can create similar audiences based on your existing remarketing lists or customer lists. These audiences consist of users who share similar characteristics and online behaviours with your existing customers or website visitors.
- Engagement Remarketing: This type of remarketing targets users who have engaged with your content, such as liking your YouTube videos, following your social media profiles, or interacting with your app, but haven't completed a conversion action.
- Dynamic Prospect Remarketing: This is a more advanced form of dynamic remarketing that targets users who have never visited your website but have shown an interest in products or services similar to yours on other websites.
- Sequential Remarketing: This strategy involves showing a series of ads to users in a specific order to guide them through a sales funnel. It can be effective for nurturing leads and encouraging conversions over time.
- Abandoned Cart Remarketing: This targets users who added products to their shopping cart but still need to complete the purchase. It reminds them of their abandoned items and encourages them to complete the transaction.
- Location-Based Remarketing: You can target users who have visited specific physical locations, such as your retail store or event venues, with tailored ads to encourage them to take further action.
5. What are the Various Methods of Collecting User Data for Remarketing Purposes, and How Do You Use This Data in Your Campaigns?
Collecting user data for remarketing purposes is a crucial aspect of digital marketing, as it allows you to target individuals who have already shown interest in your products or services.
Here are some standard methods and strategies:
- Facebook Pixel: Install the Facebook Pixel on your website to track user interactions. It collects data on page views, product views, and completed actions (like purchases). You can create custom audiences based on this data for targeted ad campaigns.
- Google Analytics Remarketing: Use Google Analytics to track user behavior on your website and create remarketing audiences based on specific actions, such as pages visited, time spent on site, and conversion goals.
- Email Marketing: Collect email addresses through sign-up forms, lead magnets, or newsletter subscriptions. Segment your email list based on user behavior and preferences. You can then create email remarketing campaigns tailored to these segments.
- CRM Data: Use Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software to track and store customer information, including their interactions with your business. This data can be used for personalized remarketing campaigns.
- Behavioral Targeting: Analyse user behavior on your website to determine their interests and preferences. You can then use this data to serve relevant ads on various platforms, such as Google Ads and social media.
- Retargeting Cookies: Implement retargeting cookies on your website to track users across the web. When a user visits your site and leaves, these cookies can trigger ads on other websites they visit, reminding them of your products or services.
- App Data: If you have a mobile app, collect data on user interactions within the app. Use this data to create in-app ads or push notifications to re-engage users who have abandoned the app.
- Social Media Engagement: Analyse user engagement on social media platforms. Platforms like Facebook and Instagram allow you to create custom audiences based on engagement, such as users who have engaged with your posts or visited your social media profiles.
- Third-party Data Providers: Partner with data providers to access third-party data that can enrich your audience targeting. This data can include demographic and behavioral insights.



